Introduction
Morbidity and mortality rate of population in United States suffering from heart disease is high, and utilization of computerized surveillance systems can effectively assist in mitigation and diagnosis of the disease before its occurrence. However, the difficulty facing health practitioners in CHD suggest that the occurrence of heart attack is uncertain, and simultaneously numerous factors are at play, which are beyond the comprehension ability of the practitioners. Although, lack of research in the field suggest that the computerized surveillance systems require further research; and, utilization of Big Data Analytics, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Internet of Things (IoT) is extremely useful in gaining precision during the process of CHD diagnosis and prevention.
Epidemiological Issues in Heart-related Diseases
Epidemiology is a scientific method in usage for performing assessment of the diseases and health outcomes in the population; and instead of treating patient and individuals as patients, epidemiology collectively refers them as communities and individuals, respectively. “Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)” defines epidemiology as, “… the study (scientific, systematic, and data-driven) of the distribution (frequency, pattern) and determinants (causes, risk factors) of health-related states and events (not just diseases) in specified populations (neighborhood, school, city, state, country, and global” (2016). Subsequently, CDC mentions the application of the study for control of problems related to health. Epidemiological issues include diagnosis, prevention, prognosis, prevalence, etiology, management, treatment, and early detection (World Health Organization, 2007). Heart diseases are also known as cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), which effects blood vessels or the heart. An increased risk of blood clots due to CVDs is primarily due to fatty deposits in the arteries (atherosclerosis). Few of the critical risk factors associated with CVDs are tobacco hypertension, smoking, and obesity.
The existing literature on CVDs suggest that it is the leading cause of mortality around the world (Shi et al., 2016). Heart patients following stroke are at higher risk of “Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)”. One of the major individual contributor to capitulation of CVDs is the living condition of people living below poverty line, coupled with malnutrition across low and middle income households with an alarming rate of eighty percent target population. Factors responsible for CVDs and CHDs in elderly and young population included, but not limited to, tuberculosis, obesity, nutritional disorders, infectious diseases, smoking, high level of sugar and salt intake in nutrition, excessive alcohol consumption, high blood pressure, human immunodeficiency, and even malaria. Shi et al. (2019) highlights the importance of Mediterranean diet for prevention and of heart diseases, which is associated with healthier heart and health, and contains high nutrition values within cereals, fruits, nuts, legumes, fish, unsaturated fats like olive oil, and grains.
Prevention and Treatment of Heart Disease
One of the leading cause of mortality and morbidity is “Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)”. The existing literature suggest that understanding of risk factors, availability of inexpensive cholesterol screening at widespread level, and the availability of effective agents that are cholesterol screening agents in well-tolerated manner remained in effective in reducing the staggering figures for mortality and morbidity rate in United States within healthcare sector (LaRosa, 2001). The better understanding of issues, and there respective diagnosis methodology, created further controversies regarding the prioritization of target population for secondary and primary prevention of events, that is, with respect to age and other variables. Amongst agents, LaRosa (2001) argues that statin class of lipid-lowering agents have both, effectiveness and tolerance. The recurrence of coronary events call for secondary prevention for established CHD and hypercholesterolemia. The controversies of primary prevention for CHD pertains to different age group of patients; however, patients with diabetes are exception, and the primary reason for the need of urgency is the risk of dramatically developing CHD. Although, patient groups require different treatment and prevention strategy, ongoing trials are going to resolve the controversies (LaRosa, 2001).
Additionally, there are numerous ways which mostly include lifestyle changes, and steps that a person can take for reduction and prevention of the CHD development, that includes: reducing tobacco smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, maintaining healthy and balanced diet, awareness of risk factors, maintaining healthy weight of body, regularity of physical exercise, maintaining healthy blood cholesterol levels, and effectively treating existing medical conditions, such as high blood pressure and type 2 diabetes. The most critical factors for prevention of CHD are education and self-awareness or mindfulness. On the other hand, test results define the treatment plan for the patients of CHD, which includes coronary angioplasty, medication, and surgery for coronary artery bypass. Nevertheless, treatment assists in reducing and elimination of the risk of heart attack, and symptoms.
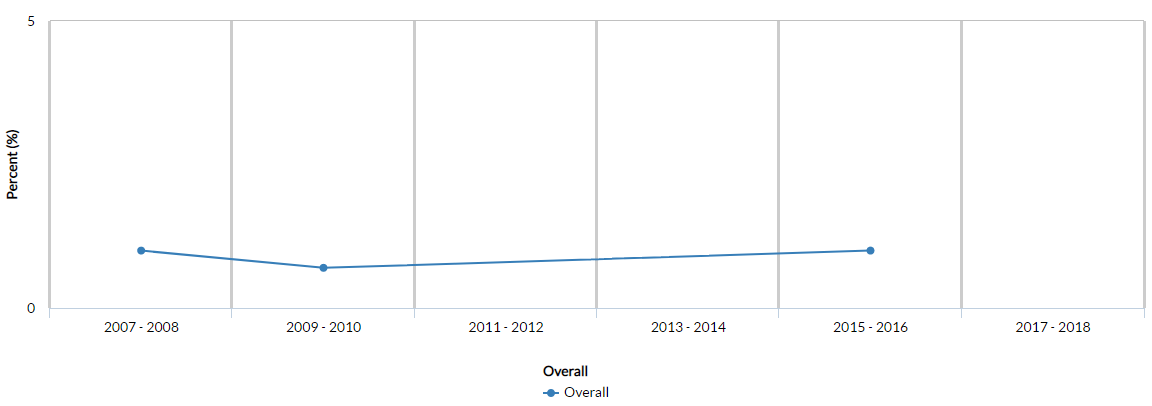
Figure 1: Prevalence of CHD in United States (overall).
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2017-18)
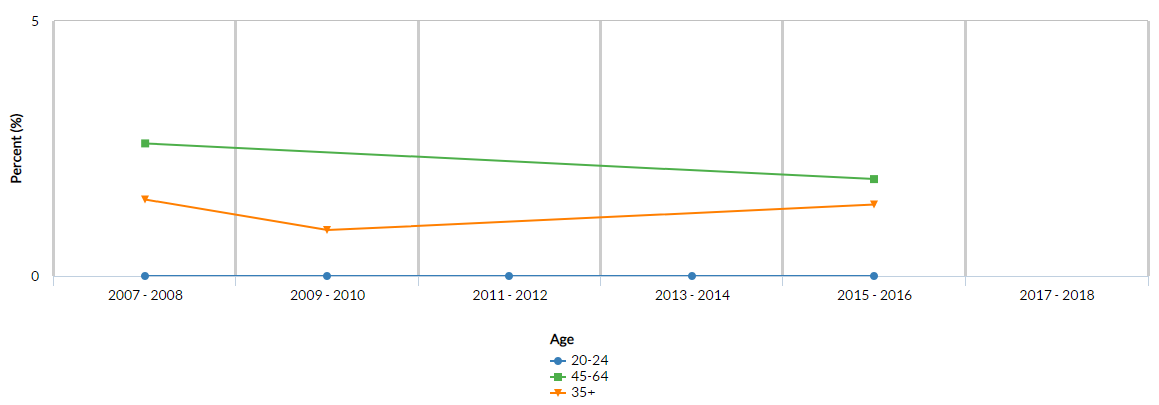
Figure No. 1 shows the data for prevalence of poor Cardiovascular Health for all available years, which indicate the scarcity of data on the subject matter. As per the statistics, the figures for the year 2007-08, 2009-10, and 2015-16 shows relatively stable graph with one percent prevalence percentage with exception of the second year, which shows 0.7 percent figure. Data for gender and age are not available, and reflects the need of computerized systems for surveillance purpose within patient population of CHD. In the similar way, data on the age bracket of between 20 and 24, and 45-64 is presented in graphical manner in the Figure 2, which suggest higher prevalence rate for older people and lower for young population.
Figure 2: Prevalence of CHD in United States
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2017-18)
Computer Surveillance Systems
The existing literature on computer surveillance systems for health disease is scarce; however, Tama et al. (2020) suggest that improving the existing intelligent detection system for CHD is possible with two-tier classifier ensemble. The occurrence of heart attack event is mostly without any prior symptoms, which brings the debate to CHD detection methods. The utilization of machine learning, and big data analytics, is extremely useful as an intelligent detection method, which Tama et al. (2020) introduces as two-tier classifier ensemble. Physicians find it difficult to account for too many factors during the diagnosis process of heart disease, which can effectively reduce with the assistance of Internet of Things (IoT) for healthcare services. Abdel- Abdel-Basset et al. (2019) research analysis suggest a novel framework which supplements the computer supported diagnosis, coupled with Internet of Things, for monitoring and detection of CHD in patients. Author lays out limitation of the existing healthcare system in diagnosis of CHS due to defectiveness and ambiguity of information. For example, the introduction of Neutrosophic multi criteria decision making (NMCDM) is the technique that can assist physicians during the diagnosis process of CHD.
Population Health Implications
Healthcare applications based on Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) provide opportunity for healthcare practitioners and patients, alike. The neutrosophic multi criteria decision making (NMCDM) technique provides element of precision in the process of diagnosis, which can be effective in reducing the cost and burden of staggering number of people suffering from CHD within United States. The introduction of computerized surveillance system influences the population in numerous ways, which includes utilization of data on symptoms to effectively detect issues of possible heart attack through healthcare applications. The percentage of people suffering from CHD is one percent of the total population in United States, and the staggering figures suggest that critical evaluation of computerized surveillance system can be used effectively for providing service deliver to the patients in primary and secondary health care setting. Lack of research in the area of computerized surveillance system suggest assessment of the existing practice in healthcare settings for diagnosis and treatment of CHD. One of the benefit for utilization of the computerized technique is to assist the process of diagnosis in an efficient and precise manner, which is the difficult facing health practitioners and patients, alike.
Conclusion & Recommendations
The heart disease rates are high in the United States, and the need for adopting Information and Communication Technologies, and combining them with artificial intelligence, highlights the adoption of computerized surveillance system. Nevertheless, the effective method for prevention of CHD among masses is the adoption of healthy routine and diet. The healthcare sector of United States lacks efficiency, and providing quality service to the population suffering from health diseases raises concerns amongst policy makers for alternative methods of diagnosis and prevention. In the paper, the existing literature highlights the importance of utilizing internet application for gaining precision in the process of diagnosis, and the lack of utilization deprives healthcare system of the opportunity to lower the burden, and complexity of the disease diagnosis and prevention, for healthcare physicians. Future informatics strategies for prevention and detection of heart diseases need to focus on exploitation of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in conjunction with the Internet of Things (IoT). However, the lack of literature on the computerized surveillance system for CHD suggest that the policy maker’s agenda should be focusing on the utilization of modern tools and techniques for facilitating various stakeholder to the CHD.
References
Abdel-Basset, M., Gamal, A., Manogaran, G., & Long, H. V. (2019). A novel group decision making model based on neutrosophic sets for heart disease diagnosis. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 1-26.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Division for Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention. DHDSP Data Trends & Maps [online]. 2015. [accessed May 12, 2021]. URL: https://www.cdc.gov/dhdsp/maps/dtm/index.html.
LaRosa, J. C. (2001). Prevention and treatment of coronary heart disease: who benefits?. Circulation, 104(14), 1688-1692.
Shi, A., Tao, Z., Wei, P., & Zhao, J. (2016). Epidemiological aspects of heart diseases. Experimental and therapeutic medicine, 12(3), 1645-1650.
Tama, B. A., Im, S., & Lee, S. (2020). Improving an intelligent detection system for coronary heart disease using a two-tier classifier ensemble. BioMed Research International, 2020.
What is Epidemiology? (2016, June 17). Https://Www.cdc.gov/; Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). https://www.cdc.gov/careerpaths/k12teacherroadmap/epidemiology.html