Introduction
The 20th century has brought a major shift in the business operations of all organizations, which are now focused on digital transformation to not only optimize their business activities but also meet the continuously changing consumer expectations (George, Lakhani, and Puranam, 2020). Although, for most organizations, this digital transformation is a key source of several new opportunities to grow themselves in the market and sustain their progress, it is an extremely difficult task to merge new technologies into the existing processes. This is evident from the global situation caused by COVID -19, which has disturbed economic activities all over the world and has forced organizations to adopt digital ways of communication and business management (George, Lakhani, and Puranam, 2020). However, it has also brought many challenges, especially for the technology industry, which has observed unprecedented changes in the customer’s behavior and thereby is struggling to align its business processes with the technological expectations.
Soto-Acosta (2020) has explained this fact by using the term “digital economy”. The digital economy is primarily affected by digital technologies such as mobile connectivity, internet, cloud computing, machine learning, big data, blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), smart manufacturing, robotics, and predictive and data analytics to completely transform the interactions, business models and activities from a digital perspective. Furthermore, the emergence of these new technologies, as he argued, has also blurred the line between industries, and therefore, tech companies are leading the retail and hospitality industries (Soto-Acosta, 2020).
Innovation has become an essential factor for the sustainable growth of tech companies. This is evident from the business icons of the past, for example, Xerox, Kodak, Nokia, Yahoo, Blockbuster, Segway, IBM, JC Penny Tie Rack, Blackberry, Commodore, and many others which failed to innovate themselves, and in a result fell from grace (Andriole, 2020). However, this is the fundamental responsibility of investors, shareholders, managers, and employees all together to realize the importance of embedding new technologies in their business models and assess specific outcomes and potential risks of this digital transformation to ensure a competitive advantage in the market.
In this regard, the following whitepaper provides a comprehensive analysis of the different internal and external factors that can influence the digital transformation process in the technology industry while highlighting the importance of innovative culture, collaborative and visionary leadership, and motivating the workforce to implement the emerging technologies successfully. Furthermore, the remarkable role of collecting and analyzing relevant data in making strategic decisions is described to make organizations completely data-driven and digitally mature. Finally, recommendations are made for the technological sector to transform their business process in the review of stated key factors.
External and internal factors of the technological sector
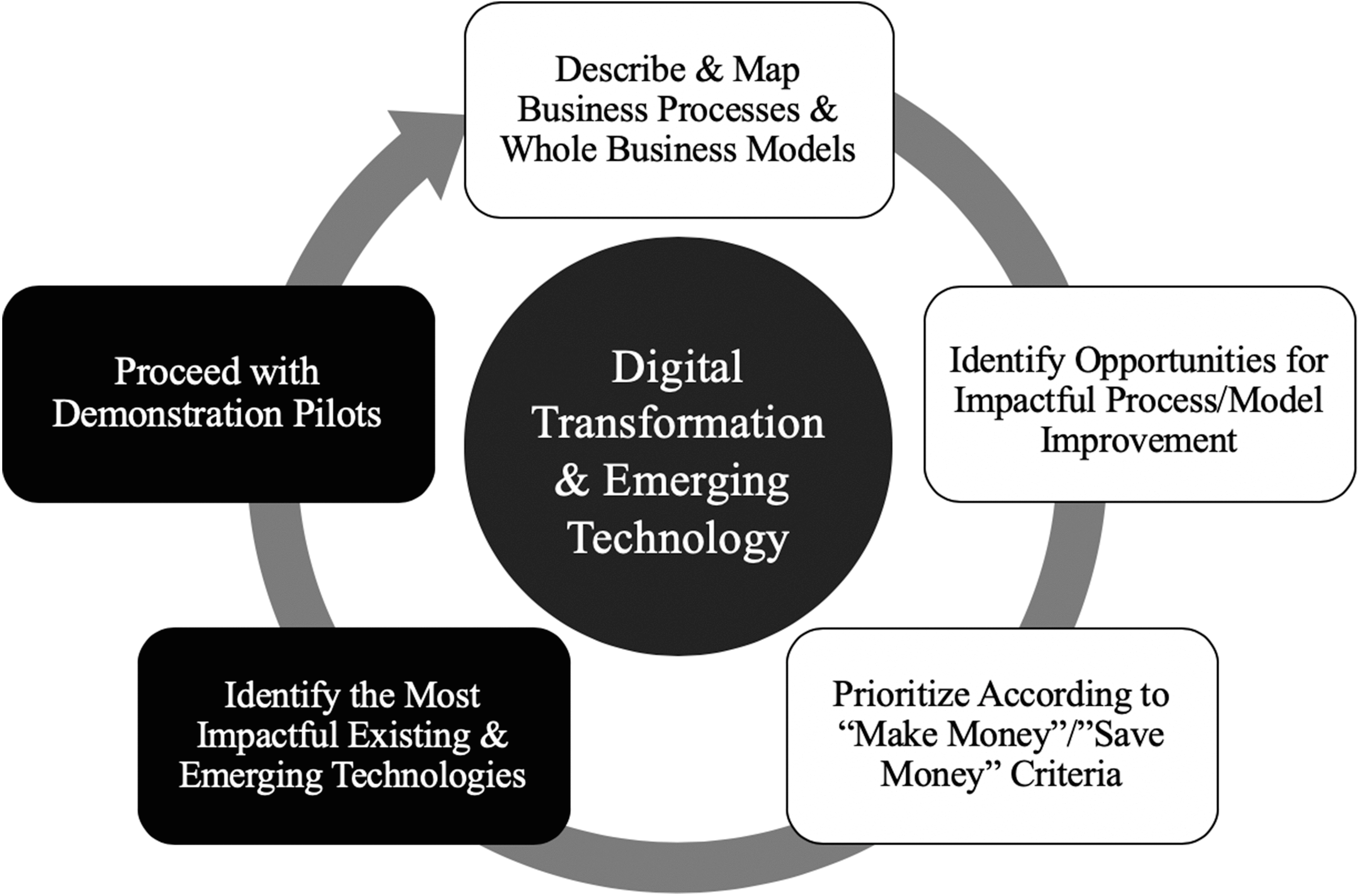
Many factors are constantly disturbing the technological sector and therefore bringing new opportunities for innovation. So, before making a firm decision to transform any business model, it is very crucial to comprehend these factors thoroughly and make decisions accordingly. For instance, the economic challenge faced by any particular industry in the market is the foremost reason for its determination of digital transformation, being its inevitable choice (XIAOHAN, 2020). The intense market competition is the second factor that motivates tech companies to focus on digital transformation for sustainable growth by responding rapidly to market changes and assembling required digital resources efficiently. Similarly, the growing customer demand for more sophisticated and advanced products is another crucial factor for tech enterprises to integrate emerging technologies into their business processes and construct a digital ecosystem that ensures productivity and efficiency. In this regard, Andriole (2020) emphasized the correct understanding of the business opportunities and mapped them with the emerging technologies to rank in the market as described in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Digital Transformation and Emerging Technology (Andriole, 2020)
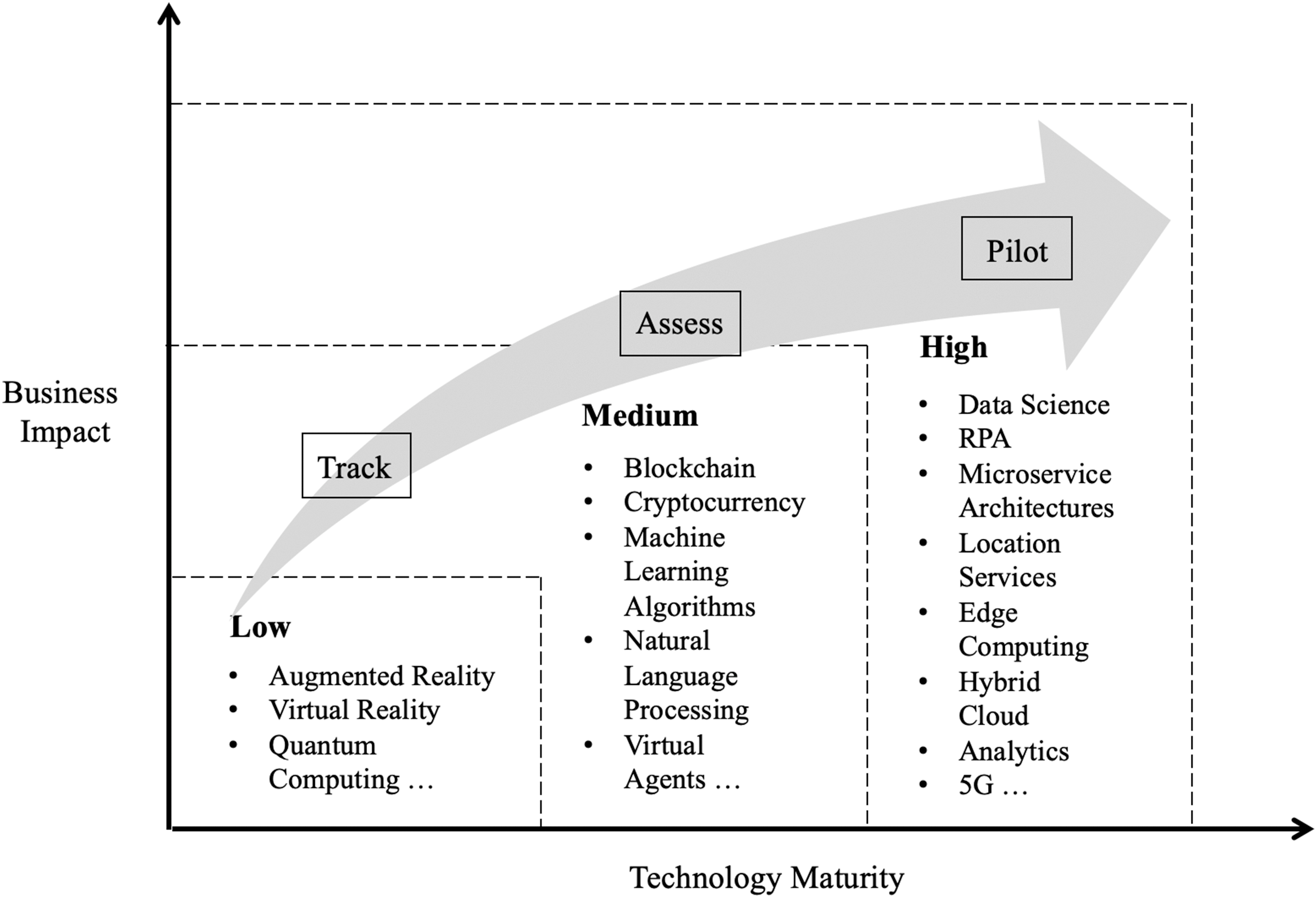
The Key emerging technologies for tech industries are hybrid-cloud, which is the biggest support for the digital transformation; multi-cloud, which helps to evaluate multiple vendors simultaneously; cloud securities which ensure the standardized protection of the data and AI capabilities which integrates the most advanced solutions. However, firstly, it is important to assess the maturity of different technologies and their business impact with respect to the specific tech industry. In this regard, the notational technology investment guide as shown in Figure 2, is very helpful in making a decision. Moreover, organizations should adopt technology roadmaps to transform themselves into industry 4.0 (Sarvari et al., 2017).
Figure 2: Notional Technology Investment Guide (Andriole, 2020)
Digital transformation is significantly different from digital changes as it involves the entire process of innovative product design, its smart and intelligent manufacturing, and value-added service delivery. In this regard, XIAOHAN (2020) indicates five important dimensions of technological transformation i.e. operations optimization, customers’ participation in improving business processes, digital empowerment of personnel, digital economic business development strategy, and openness of business processes. However, the technological sector is prone to many business challenges such as cognitive dislocation, unclear stages, organizational structure, performance evaluation, and underbudgeting, which distinctly influence its effective digital transformation. For example, if top management does not have a long-term strategy for transforming the organization and precise knowledge of the current stage of transformation in the sector, the results will be devastating. Because only they can formulate the required organizational structure and key performance indicators to integrate and innovate resources. Therefore, this important role of workforce, leadership, and culture is discussed in the following section.
The role of people (workforce, leadership, and culture)
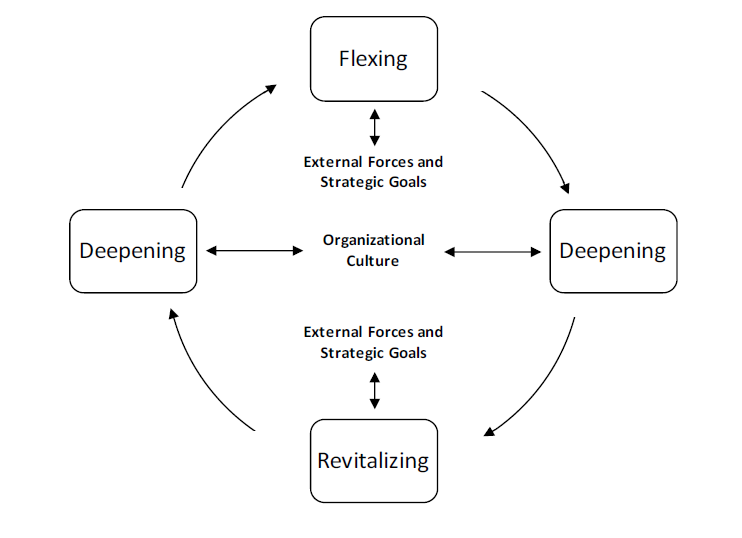
Digital transformation is directly linked with workforce transformation because it involves the reconstruction of business processes, roles, and services from the perspective of the technology to redesign the human resource management practices (Eden et al., 2019). Therefore, to assist managers in transforming their workforce, Eden et al. (2019) presented a workforce transformation model (as shown in Figure 3) consisting of flexing, deepening, and revitalizing their interrelationships. Flexing is the response of employees and organizations towards external challenges and pressures to mitigate their effect on the existing structures and resources while deepening is the self-improvement of the workforce to develop future strategies. Revitalizing requires the workforce and organization to adopt permanent changes in the structure and roles. These are the fundamental steps for workforce transformation.
Figure 3: Workforce Transformation Model (Eden et al., 2019)
However, to deploy effective workforce management strategies, develop the required human resource and make support the strategic decision, the role of managers is very crucial. Digitalization and globalization, on the one hand, has urged managers to implement emerging technologies for the reconstruction of business model, while on the hand, has highlighted the growing importance of effective human resource management to incorporate emerging HR trends.
Therefore, for the digital transformation of the technology sector, it is vital to develop an organizational culture that promotes and sustains innovation by attracting talented human capital. This has become one of the primary measures of competitive advantage in the market. For instance, in the ongoing situation of the pandemic, when many organizations communicate with their employees digitally by implementing effective strategies of “work from home, there are also many industries that failed to develop such resources. While COVID 19 has only accelerated the pace of digital transformation, we have observed the inefficiency of the existing organizational culture in utilizing emerging technologies effectively. So, making the entire set-up of the organization digital will bring many challenges and uncertainties which can only be coped with a resilient workplace environment and effective leadership. Therefore, Soto-Acosta (2020) states that “the question is not whether to replace the human workforce with machines, but how technology can be leveraged to allow employees to do their work more effectively”.
In brief, for the successful integration of emerging technologies to digitally transform the technological sector, the managers need to play the role of leaders to manage a diverse coherent workforce by thinking beyond technical skills only. They need to provide their employees with opportunities to strengthen their data analysis, data visualization skills, agile project management, data-centric decision-making skills, emotional intelligence, innovative thinking, design thinking, analytical thinking, and strategic planning and forecasting. This will also ensure that the organizational culture is developed enough to intergrade innovation and sustain progress by focusing on set targets.
The value of data (transparency and data sources)
Digital transformation aims to make organizations completely data-driven and knowledge-based. Moreover, for management to make any strategic decision, evaluate business progress, forecast business risks, and develop strategies to mitigate them, the collection and analysis of the relevant data is necessary. In this regard, there are various methods to collect data for an organization’s daily operations and innovation. These include data from customers’ experiences with the use of products or services, industry trend data, market change data, forming panoramas of its daily operations, market changes, and industry trends to improve its operational efficiency and create new business models.
However, it is also the responsibility of the organizations to protect customers’ data as with the increasing usage of emerging technologies, all kinds of interactions between consumers and the organization are controlled digitally. For the tech industry, whose activities are entirely based on customers’ data, it becomes even more important that the tech industry is very transparent in its policies to earn the trust of its customers. Therefore, consumers of tech industries are now very conscious about how their private data, including their details and online activities, are being used. So, if the consumers’ data is very beneficial for effective marketing and serviceability, it can also bring disaster to the business if customers’ trust is broken.
Therefore, if data is considered as ‘oil’, the trust becomes high-value currency because, in the case of digital transformation, the key element for the success of any business would be how customer values their services. This is also a reason for the increasing competition of companies in the tech industry because consumers prioritize those industries which protect their data and use it ethically. Thus, data transparency plays a leading role in the successful digital transformation.
However, as more and more data are collected, it becomes a challenging task to manage it effectively and provide simultaneous access to different stakeholders. Moreover, different organizations use different data sources based on the products or services they provide and, therefore, need customized data handling techniques (Sun et al., 2020). So, for any industry to realize digital transformation, the corresponding frameworks of data management must be developed and improved in an environment where systems, processes, and people are all connected digitally along with ensuring that the consumer’s data is not compromised.
Conclusion and recommendations
From the above discussion, the growing importance of integrating emerging technologies in business operations is evident. The technological industry has seen a massive shift in the consumers’ expectations and demands, especially in the current dynamic environment of the 20th century. Moreover, COVID-19, despite its economic and social disruptions, has stimulated the industries’ willingness and efforts to digitally transform themselves. However, the sudden and unforeseen changes in the business environment of many industries have also shown the fragility of existing business models in dealing with uncertain circumstances.
Therefore, for any tech industry which is aimed at digital transformation, the in-depth understanding of both internal and external factors is very decisive as it provides a vision for the organization to implement certain technological changes. In this regard, hybrid cloud, multi-cloud, cloud security, and AI capabilities are key technologies for digital transformation. However, successful transformation is only possible when business managers exhibit excellent leadership skills to train and manage the workforce in a coherent and diverse business environment. Also, with changing business environment, industries must consider the different challenges that can emerge with the use of technologies and devise mitigating strategies accordingly. For example, in the digital world, all business activities are data-driven and therefore, problems can arise related to data management and data security when several stakeholders would have simultaneous access. Companies themselves must have transparent policies regarding the consumers’ data to earn their trust, which will be the sole factor for the competitive advantage in the market.
Thus, it is recommended for organizations to redesign their business models and strategies to cope with the challenges towards their way to digital transformation and adapt to constant technological advancements to stay up to date. For this purpose, businesses need to collaborate to come up with the most efficient solutions. Also, the technological sector needs to adopt the “Everything-As-A-Service” model which is focused on cloud adoption to strengthen the customers’ experience with products and services.
References
Andriole, S.J. (2020). Innovation, Emerging Technology, and Digital Transformation. IT Professional, [online] 22(4), pp.69–72. Available at: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9143257/ [Accessed 27 Jul. 2020].
Eden, R., Burton-Jones, A., Casey, V. and Draheim, M. (2019). Digital Transformation Requires Workforce Transformation. MIS Quarterly Executive, 18(1).
George, G., Lakhani, K.R. and Puranam, P. (2020). What has changed? The Impact of Covid Pandemic on the Technology and Innovation Management Research Agenda. Journal of Management Studies.
Sarvari, P.A., Ustundag, A., Cevikcan, E., Kaya, I. and Cebi, S. (2017). Technology Roadmap for Industry 4.0. Springer Series in Advanced Manufacturing, pp.95–103.
Soto-Acosta, P. (2020). COVID-19 Pandemic: Shifting Digital Transformation to a High-Speed Gear. Information Systems Management, pp.1–7.
Sun, S., Zheng, X., Villalba-Díez, J. and Ordieres-Meré, J. (2020). Data Handling in Industry 4.0: Interoperability Based on Distributed Ledger Technology. Sensors, 20(11), p.3046.
XIAOHAN, S. (2020). Customer Participation in Digital Transformation, Value Co-Creation and Firm Performance: An Empirical Study in China Information Communication & Technology Industry. [Doctoral Thesis] Available at: https://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.806066 [Accessed 3 Nov. 2020].