Introduction
Consumers’ behavior is rapidly changing in the 21st century with the advent of new information technologies. Therefore, the conventional way of shopping is also being replaced with online shopping all over the world. According to Nanduri et al. (2020a) and Thaseen et al. (2021), e-commerce will reach $4 trillion in 2021 and is becoming the fastest growing sector in the world. Therefore, almost all kind of businesses are making their utmost efforts to innovate their work strategies by offering their products and services online. Similarly, different banks and other financial institutions have devised ways for the transaction of online payments which primarily include the use of credit and debit cards instead of cash.
However, with the growing number of online transactions, the number of online frauds has also increased significantly. Therefore, Diadiushkin, Sandkuhl and Maiatin (2019) highlighted that as much as there is a need to offer a company’s products online, there is a need to integrate sophisticated and advanced fraud prevention system to avoid losses at online marketplace. The online payment process has different steps during which hackers and scammers can find ways to make fake transactions and as the size of the online market increases the risk of such attacks also increases accordingly (Zhou et al., 2019).
It is further important to highlight that consumers often make payment through different digital devices, but mobile phones are most widely used because of their convenience however, they are more vulnerable to security attacks (Vishwakarma, Tripathy and Vemuru, 2021). Therefore, companies and businesses which are offering their services or products online must ensure that they are using the most advanced payment transaction to prevent any kind of attacks by the expert fraudsters (Shimpi, 2016). However, integrating a new system can involve some cost and other deliverables that may slow down the online business activities for some time. But considering the cost of online frauds, the companies can save a huge sum of money being lost in such scams and frauds.
In this regard, the following report presents a project plan and strategy for implementing a new fraud prevention system on an online merchant platform by also highlighting the risk assessment in the form of different kinds of project setbacks and their prevention and control strategies.
Project Plan
Before making a complete project plan, it is first important to investigate what is meant by fraud prevention. In this regard, Larkin (2012) mentioned that preventing online transaction fraud includes: data processing terminals, means for receiving and filtering the electronic request for a transaction, parameters for indicating whether the transaction is fraudulent and finally the method to process the transaction with the cardholder’s account data. To achieve this, there are different machine learning models available that can potentially tackle the challenge of detecting and preventing fraud patterns as described by Nanduri et al., 2020). To make these prevention strategies more accurate, different institutions involved in the transaction process can also use many strategies such as the manual review of the transactions. However, this project is based on fraud prevention by integrating the machine learning model in the online marketplace.
Schedule
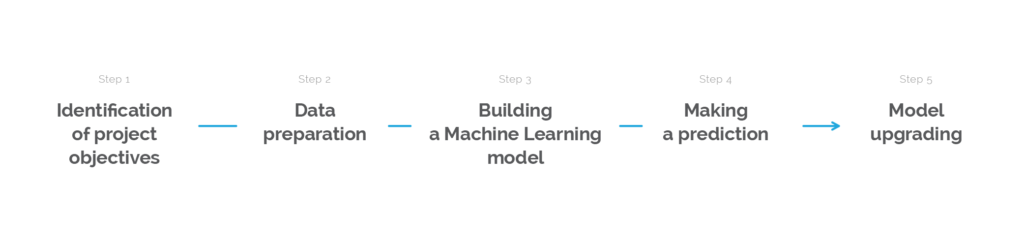
The basic project plan for integrating the machine learning model in the transaction process includes five steps as shown in Figure 1. These are the identification of project objectives, data collection, development of machine learning model, making a prediction and model up-gradation.
Figure 1: Steps for the integration of machine learning model
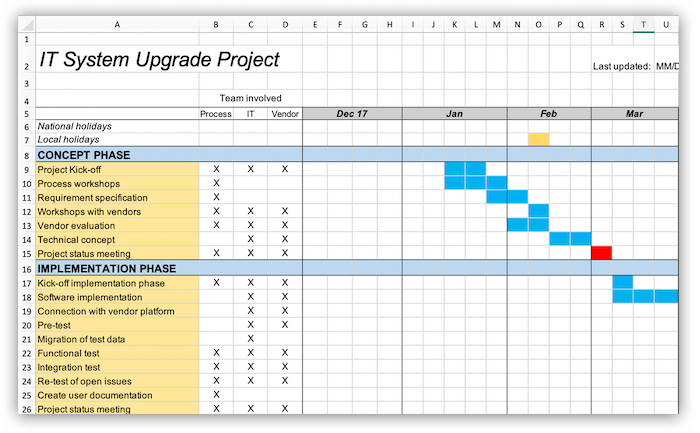
However, since the project plan includes the timelines, resources and different activities, a more detailed schedule is presented in Figure 2, which describes the work breakdown structure of the project. The main activities of the project are divided into two categories of concept phase and the implementation phase. Further, the relevant human resource is also indicated against each activity along with the expected time required to complete this. The timeline of the project consists of almost three months, but the project exact time is mainly dependent on the test results of the software because further activities will be performed based on how software is valued. These activities are mentioned WBS in the implementation phase.
Figure 2: Work breakdown structure
Cost
Cost and time are the most important factors in determining the success of any project (de Wit, 1988). However, as stated above, the success of this project is also dependent on how the initial model of the software is evaluated in the first test. So, based on the results, the time and the cost of the project can increase significantly. Furthermore, the machine learning model needs continuous updates to effectively detect fraud prevention patterns which always change over time. The hackers and fraudsters also constantly invent new technologies to steal the personal data of the consumers and make fake purchases which again requires the fraud prevention system to be constantly upgraded and improved to mitigate such risks. Thus, the project is continuous where a team of IT experts will investigate the effectiveness of the new system against new frauds and will improve it accordingly.
Therefore, based on the size of the online marketplace, the number of consumers using the platform and the complexity of the prevention system, the cost will be determined accordingly.
Quality Goals and Control Procedures
Throughout the planning and the implementation phase of the project, there may arise many issues that can potentially lead to the failure of the project if they are addressed in the meantime. Therefore, quality assurance is an integral part of any project to avoid any big losses in the form or time or cost in the later stages of the project. In this regard, a suitable strategy for quality assurance is needed. So, considering the complexity of this project, the quality control process will consist of three types of evaluations: initial evaluation, ongoing evaluation and deliverable evaluation (Zwikael and Meredith, 2019).
The initial evaluation investigates if the project has the right plan, resources and other supporting details. In this regard, the documentation of all the processes and the procedures are very important so that the project objectives are very clear to all the personnel working on the project. Similarly, it is also important that all the stakeholders of the project share the same agenda and are completely informed about the scope baseline and financial baseline of the project. Once the complete project plan is outlined and shared with the stakeholders, the implementation phase starts, which involves the ongoing evaluations. In this regard, a weekly report will be conducted to track down the progress and all the activities of the project. It will be tracked down in the software containing the expected delivery dates to record if there are any deviations.
However, in this phase, several problems such as the changings in the scope baseline, resource availability, technical issues and setbacks in the development of the software may occur. Therefore, to control and effectively respond to these challenges, a proper risk management strategy will be implemented. Finally, in the delivery evaluation, the whole project will be reviewed by the technology expert to analyze if the project meets the desired objectives. Similarly, the readiness reviews will also be conducted in this evaluation to decide whether the new system has to offer to the customers or not.
Key Project Roles
As described in WBS, the key project roles are distributed as IT experts, project administrators and vendors. The main responsibility of the administrators is to execute the project according to its desired timelines and objectives while establishing strong communication between different stakeholders. The IT experts are mainly responsible for the development of the software and handling of all the technical aspects of the project. They also need to communicate the different materials; tools are equipment they require to perform their job to administrators so they can effectively and efficiently manage their supply from the different vendors. This way, all the key personnel work together to ensure the successful execution of the project.
Risk Assessment and Control Process
During the lifetime of the project, several setbacks can occur which if not managed effectively can lead to higher losses (Junkes, Tereso and Afonso, 2015). Therefore, the managers specifically need to adopt the most effective approach to control the risk and ensure successful project delivery. In this regard, consider for example that the software does not satisfy the testing requirements and as explained in the earlier sections this can badly affect the project’s overall performance. However, this also does not mean that all the previous efforts made by the development team are useless. Instead, to handle the situation effectively and maintain the same motivation level as the developers, the manager needs to acknowledge their efforts and motivate them to consider other innovative ways to prevent the failure of the software.
Secondly, any software is inherently prone to failure during the first testing and this risk is always there while executing such projects (Fairley, 1990). Therefore, the manager should pay careful attention to different strategies that can help them identify and prioritize the risks. Moreover, the risk assessment and the control process should also be the central activity to generate the most suitable response to different time and cost constraints. This risk assessment and control process can be further divided into two steps of monitoring and mitigating. Monitoring includes publishing the project status reports which include the risk management issues, continuously revising the risk plans based on the project schedule, reviewing and prioritizing the risks and brainstorming the potential risks. The mitigation process includes assessing the impact of the risk, adjusting the project scope and schedule, accordingly, taking the most suitable action in time and continuously monitoring the effectiveness of the action. This is the most appropriate approach to effectively respond to any kind of risk during the entire project life cycle.
Conclusion
Project planning and management is an essential part of any business growth strategy because companies cannot sustain their growth and mitigate the different risks that can impact their business activities. Considering the importance of the project plan, this report has outlined the various aspects of project management while highlighting the importance of different tools for project management that enable managers to do realistic project planning. Moreover, the project management performed this way can greatly improve the effectiveness of the projects because of conveniently implementing the quality control procedures which further results in the reduced costs.
The focus of this report is to develop a project plan and strategy for the implementation of a new fraud prevention system on e-commerce platforms. And considering the importance of the project management tool, we used an online tool to generate the Gantt chart which exhibits the different activities of the project along with the timelines and resource allocation. The managers can easily track down the progress of the project by referring to this Gantt chart and improve the project execution process. This way the project can be executed in an optimum way.
References
AltexSoft. (2018). How to Choose Fraud Detection Software: Features, Characteristics, Key Providers. [online] Available at: https://www.altexsoft.com/blog/business/how-to-choose-fraud-detection-software-features-characteristics-key-providers/ [Accessed 15 Feb. 2021].
Baig, A. and Reddy, K.Nagi. (2020). UTILIZING PRODUCT FEATURES FOR FRAUD DETECTION ON E-COMMERCE PLATFORMS IN BIG DATA TRANSACTIONS.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCE SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH AND
ENGINEERING TRENDS, [online] 5(11). Available at: http://ijasret.com/VolumeArticles/FullTextPDF/595_8.
UTILIZING_PRODUCT_FEATURES_FOR_FRAUD_DETECTION_090.pdf [Accessed 15 Feb. 2021].
de Wit, A. (1988). Measurement of project success. International Journal of Project Management, 6(3), pp.164–170.
Diadiushkin, A., Sandkuhl, K. and Maiatin, A. (2019). Fraud Detection in Payments Transactions: Overview of Existing Approaches and Usage for Instant Payments.
Complex Systems Informatics and Modeling Quarterly, (20), pp.72–88.
Fairley, R.E. (1990). Risk Management: The Key to Successful Software Projects *. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 23(5), pp.45–50.
Junkes, M.B., Tereso, A.P. and Afonso, P.S.L.P. (2015). The Importance of Risk Assessment in the Context of Investment Project Management: A Case Study. Procedia Computer Science, 64, pp.902–910.
Larkin, C. (2012). MERCHANT ALERT SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR FRAUD PREVENTION. [online] Available at: https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/d4/5d/69/
a89498e0a49480/US20120047072A1.pdf [Accessed 15 Feb. 2021].
Nanduri, J., Jia, Y., Oka, A., Beaver, J. and Liu, Y.-W. (2020a). Microsoft Uses Machine Learning and Optimization to Reduce E-Commerce Fraud. INFORMS Journal on Applied Analytics, 50(1), pp.64–79.
Nanduri, J., Liu, Y.-W., Yang, K. and Jia, Y. (2020b). Ecommerce Fraud Detection Through Fraud Islands and Multi-layer Machine Learning Model. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, pp.556–570.
Shimpi, P.R. (2016). Survey on Credit Card Fraud Detection Techniques. International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science.
Thaseen, S., Cherukuri, A.K., Kopparapu, A. and Velu, G. (2021). Cross-Border E-Commerce Security Issues and Protections. Cross-Border E-Commerce Marketing and Management, pp.98–119.
Vishwakarma, P.P., Tripathy, A.K. and Vemuru, S. (2021). Fraud Detection in NFC-Enabled Mobile Payments: A Comparative Analysis. Innovative Data Communication Technologies and Application, pp.397–403.
Zhou, H., Sun, G., Fu, S., Jiang, W. and Xue, J. (2019). A Scalable Approach for Fraud Detection in Online E-Commerce Transactions with Big Data Analytics. Computers, Materials & Continua, 60(1), pp.179–192.
Zwikael, O. and Meredith, J. (2019). Evaluating the Success of a Project and the Performance of Its Leaders. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, pp.1–13.