ABSTRACT
This report aims to evaluate the challenges faced by Qatar Airways regarding carbon emissions and their influence on competitive advantage in the industry. The report underlines the critical role of sustainability in preserving market presence and customer loyalty by examining the airline’s existing strategies, such as integrating sustainable fuels and improving operational efficiency. Thus, Qatar Airways should focus on reducing carbon in operation, relying on eco-friendly practices to secure its position as a leader in the sphere of sustainable air travel.
I. INTRODUCTION
Background and Purpose of the Report
Qatar Airways, established in 1993 and relaunched in 1997, has rapidly become a global mega airline. Started by the royal family of Qatar, the airline began its humble operations in January 1994 with just one leased Airbus A310 aircraft, embarking on an illustrious voyage that would lead it to unprecedented heights (Hayward, 2021). Since then, through perseverance and exemplary service, it has risen to earn widespread acclaim, securing its place as the leader in its field. Qatar Airways has received recognition as the “World’s Best Airline” by aviation authority Skytrax, taking the coveted title an unmatched seven times between 2011 and 2022 (About Qatar Airways | Qatar Airways Newsroom, 2024). No other airline can claim such consistent dominance in passenger comfort and luxury categories, as evidenced by the carrier’s repeated victories as the “World’s Best Business Class.” Qatar Airways also took the lead as the initial Middle Eastern airline to achieve the highest standard of certification in IATA’s Environmental Assessment (IEnvA) program, adhering to internationally recognized environmental management principles (such as ISO 14001) (About Qatar Airways | Qatar Airways Newsroom, 2024). Despite these magnificent achievements, challenges remain as Qatar Airways wrestles with issues of sustainability that endanger its preeminence, such as carbon emissions, ecological impact, and fuel expenses. Qatar Airways contributes to airborne carbon like all air transport due to its extensive flight schedule. The burning of jet fuel unleashes greenhouse gases, exacerbating the climate crisis. Aviation industry growth has led to amplified noise pollution around airports, disrupted habitats, and degraded air quality. As a major operator, Qatar Airways faces scrutiny regarding its environmental footprint. Fuel represents a sizable portion of an airline’s operational costs. As the sector explores alternative fuels, Qatar Airways must balance affordability with ecological effect (Baluyut, 2022). Thus, as a prominent leader in aviation, Qatar Airways confronts increasing pressure to address its carbon emissions and contribute to global efforts to mitigate climatic alteration. As an environmental advisor, this report aims to provide insight into how carbon emissions and climate change may impact Qatar Airways’ competitive edge. Additionally, it offers recommendations for how the organization can best respond to these pressing environmental sustainability issues.
Scope and limitations of the report
While this report primarily focuses on assessing the carbon emissions related to Qatar Airways’ operations and the difficulties imposed by climate change on its competitiveness, it is essential to acknowledge the constraints inherent in implementing sustainability initiatives across the entire aviation sector. Several factors, such as regulatory restrictions, technological limitations, and economic considerations, present challenges to the feasibility and efficacy of specific emission-reducing strategies. This report aims to provide a balanced examination of the opportunities and difficulties associated with Qatar Airways’ efforts to mitigate its environmental footprint. The following sections will delve into the specifics of carbon emissions and climate change concerning Qatar Airways, explore the most constructive responses to these issues, analyze the possibilities and hurdles of implementing sustainability measures, and conclude with recommendations for future enhancements. With a more comprehensive understanding of the intricacy and range of impacts within the aviation industry, this report intends to offer insights while recognizing limitations.
II. CARBON EMISSIONS AND CLIMATE CHANGE ISSUE
Overview of carbon emissions from the aviation industry
Aviation impacts global carbon dioxide emissions, though its contribution is complex. Aviation accounts for around 2.5% of worldwide CO2 emissions (Hannah Ritchie, 2022). While this portion seems small, it represents a sizeable effect because of the sector’s scale. The discrepancy lies in the reality that air travel dominates individual contributions to climate change for frequent flyers. In contrast, many individuals do not fly due to economic barriers or other factors. Thus, aviation’s total contribution remains modest relative to other sources. Domestic flight CO2 emissions are included in national tallies. However, international flights are labeled as “bunker fuels” and fall outside any country’s accounting, removing the motivation for nations to curb aviation emissions.
The primary means by which aviation affects climate change involves CO2 emissions. Most flights rely on jet fuel, converted to CO2 upon combustion. Scholars have reconstructed annual aviation CO2 emissions dating back to 1940, revealing a rise. 2018, global aviation (passenger and freight) emitted approximately 1.04 billion metric tons of CO2 (Hannah Ritchie, 2022). Beyond CO2, aviation also has non-CO2 impacts on climate, such as contrail formation, cirrus cloud enhancement, and nitrogen oxide emissions. Considering these non-CO2 effects, aviation’s total contribution to warming equals 3.5% when measured as “effective radiative forcing”—a more accurate reflection of its impact on temperatures.
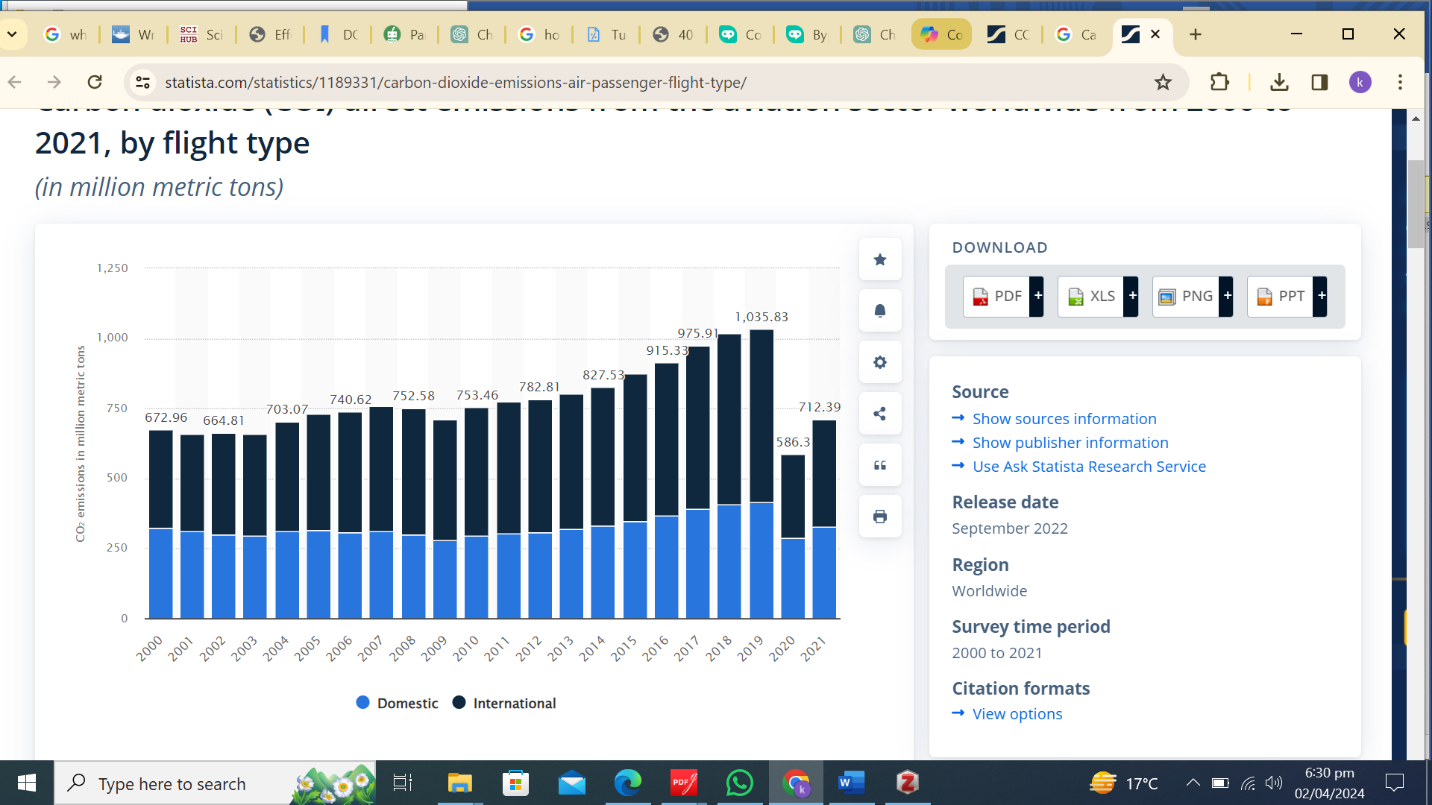
Figure 1Carbon dioxide (CO₂) direct emissions from the aviation sector worldwide from 2000 to 2021, by flight type (in million metric tons)
Specific challenges and concerns related to Qatar Airways’ carbon emissions
High Emissions Intensity:
Aviation inherently results in high carbon emissions because, with current technology, flying depends on the combustion of hydrocarbon fuels, producing carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases. Qatar Airways operates an extensive network of long-haul flights, especially those connecting distant regions, resulting in high carbon emissions attributed to these intense operations (Satyendra Pathak, 2022).
Limited Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) Availability:
Qatar Airways cannot effectively reduce carbon emissions through reliance on clean fuels such as SAF because of limitations in production capacity. The airline company can only obtain limited SAF within the regulated economy (Andrew Mills, 2023).
Fuel Efficiency and Energy Transmission:
Improving fuel efficiency is vital in minimizing carbon emissions. However, achieving significant improvement in fuel efficiency without compromising aircraft safety and performance is impossible. Qatar Airways needs to undertake research and development on optimizing the energy transmission systems to unlock gains in fuel transfer efficiency.
Human Talent for Aviation Sustainability:
Carbon emission management for Qatar Airways is a specialized area requiring professionals with expertise in environmental regulations, sustainability, and business operations. Qatar Airways has to invest in human capital to recruit and retain experts who can creatively develop, implement, and regulate their carbon emission reduction program to ensure a compliant and successful operation. At the same time, the organization can consult ATAG on various concerns, including policy influence, carbon offsets, and carbon-neutral growth (ATAG, 2021).
Potential impact of carbon emissions and climate change on Qatar Airways’ competitiveness
Reputation and Public Perception:
Airlines are increasingly measured by their ecological records, and the sustainability record of Qatar Airways affects passengers’ choices. Good repute boosts competitiveness (Qatar Airways, 2022).
Regulation and Costs:
Stricter rules concerning emissions are inevitable. Both not following them and implementing technologies needed to meet them boost costs. The first option can result in penalties, while the second will incur operation costs. In this case, short-term investment increases costs but ensures the company is competitive in the long run (John, 2021; Qatar Airways, 2022).
Market Presence and Agreements:
It has become increasingly simpler for airlines to address their ecological impact and enter international agreements. The commitment of Qatar Airways to net-zero emissions by 2050 is more in link with the global strategy, making it more relevant for markets (Qatar Airways, 2022).
Competition from Green Airlines:
Airlines that have already embraced sustainability as a policy are more competitive. Qatar Airways is competing not only with all the other players in the industry but also with some who have already assumed their responsibilities in the field. Such actions are considered when assessing the company’s status in the market (Joelyn Baluyut, 2023).
Customer Demand and Loyalty:
People who care about the environmental aspect of flying seek to travel with companies that share their ethics. Qatar Airways’ decision to be sustainable will promote loyalty and attract more passengers adhering to such values (Joelyn Baluyut, 2023).
III. BEST RESPONSES TO ADDRESS CARBON EMISSIONS AND CLIMATE CHANGE
Overview of Qatar Airways’ current carbon reduction policies and practices
Voluntary Carbon Offset Programme:
Qatar Airways launched a voluntary carbon offset program for business customers. This programme enables business and trade clients to balance their carbon emissions through a devoted web portal earlier or afterwards a flight (Qatar Airways Newsroom, 2022). The airline collaborates with the International Air Transport Association (IATA) to ensure credits bought for offsetting emissions come from independently verified projects with broader environmental and social benefits (Newspaper, 2020)
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) Integration:
Qatar Airways is the foremost airline in the Middle East and Africa to commit to SAF integration. The goal is to integrate at least 10% SAF into jet fuel consumption by 2030. SAF significantly reduces carbon emissions compared to conventional jet fuel (Joelyn Baluyut, 2023).
Fuel Optimisation Initiatives:
The airline actively optimizes fuel usage through its Environmental Management System. Projects include retaining Hamad International Airport’s certification under the Airport Carbon Accreditation Scheme and recycling consumed cooking oil to create biodiesel (John, 2020).
Environmental Policy:
Qatar Airways aims to achieve lower, more efficient greenhouse gas emissions. The airline integrates environmental requirements into procurement decisions and personal responsibilities (Environmental Sustainability | Qatar Airways, n.d.).
Recommended responses to reduce carbon emissions and mitigate climate change impacts
1. Investment in Sustainable Technologies:
Advanced Aircraft Technology:
Airlines like Qantas invest in current aircraft models with advanced aerodynamics, lightweight materials, and efficient engines. For instance, the Boeing 787 Dreamliner features a mostly composite airframe, resulting in significant fuel savings (Vasigh & Azadian, 2022). Also, Airbus A321XLR operates with 100% Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF), showcasing the potential of sustainable technologies (Lomas, 2023).
2. Scaling Up Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF):
The Qatar airline aims to integrate at least 10% SAF into jet fuel consumption by 2030 (Redactive Media Group, n.d.), and SAF will significantly reduce carbon emissions compared to conventional jet fuel. Also, Canada has invested $350 million to accelerate the green industrial conversion of the aerospace business, including SAF development, which shows the coming commitment and need for the future (Laurie Bouchard, 2023).
3. Operational Efficiency:
Fuel-Efficient Operations:
Airlines optimize flight routes, reduce taxi times, and minimize ground delays. To get the inspiration by Boeing 787-9 as it is the record fuel-efficient aircraft, operating at 39 passenger kilometers per liter of fuel, 60% well than the A380 (The Digital Evolution in Aviation, n.d.). Also, Airlines like British Airways have adopted reduced engine taxiing, saving 4,100 tons of fuel per year at their hub airport (McCausland, 2023).
4. Carbon Offsetting and Renewable Energy Projects:
Qantas and other airlines offer voluntary carbon offset programs to passengers. Passengers can compensate for their flight emissions by financing emission reduction projects elsewhere (Rune, n.d.). Also, Airlines invest in renewable energy sources such as wind farms and solar power. JetBlue Airways, Rolls-Royce, and Yokogawa are actively involved in sustainable initiatives (Sustainable et al. | Shell Global, n.d.). These initiatives show an example to Qatar Airways.
By combining these strategies, airlines contribute to a greener aviation industry and work toward achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. Collaboration, innovation, and policy support are essential for sustainable progress.
Comparison of alternatives and justification for the chosen response strategies
Table 1 Comparison of Response Strategies
| Strategy | Justification |
| 1. Investment in Sustainable Technologies | Pros: Improves fuel efficiency and reduces emissions. Cons: High upfront costs and long innovation cycles. Example: Qantas investing in advanced aircraft technology. |
| 2. Scaling Up Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) | Pros: SAF significantly reduces emissions. Cons: Limited availability, cost challenges. Example: Qatar Airways is aiming for 10% SAF integration by 2030. |
| 3. Operational Efficiency | Pros: Immediate impact, cost-effective. Cons: Requires process optimization. Example: Reduced engine taxiing by British Airways. |
| 4. Carbon Offsetting and Renewable Energy Projects | Pros: Engages passengers and complements other strategies. Cons: Relies on voluntary participation. Example: Qantas’ voluntary carbon offset program. |
IV. OPPORTUNITIES AND CHALLENGES OF IMPLEMENTING CARBON REDUCTION MEASURES
Opportunities and benefits of implementing carbon reduction measures.
a. Sustainable Technologies and Innovations:
- Opportunity: Advances in aircraft design, materials, and engine technology enable significant increases in fuel efficiency and decreased emissions.
- Benefits: Greener and more sustainable aviation, reduced operational costs, and improved competitiveness (Atul Jain, 2023).
b. Scaling Up Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF):
- Opportunity: SAF significantly reduces carbon emissions compared to conventional jet fuel.
- Benefits: Lower environmental impact, increased energy security, and potential economic benefits for SAF producers (Aviation et al. | Federal Aviation Administration, n.d.).
c. Operational Efficiency:
- Opportunity: Optimizing flight routes, reducing taxi times, and minimizing ground delays.
- Benefits: Immediate impact, cost-effectiveness, and reduced emissions (Aviation et al. | Federal Aviation Administration, n.d.).
d. Carbon Offsetting and Renewable Energy Projects:
- Opportunity: Engaging passengers and cargo clients in voluntary carbon offset programs.
- Benefits: Complements other strategies, empowers travelers, and supports emission reduction projects elsewhere (Reducing Aviation’s Impact on the Climate – Environmental Defense Fund, n.d.).
Challenges, limitations, and mitigating strategies for reducing carbon emissions in the aviation industry
a. Complexity of the Aviation Sector:
- Challenge: Unique requirements such as weightiness and size restraints, extended innovation cycles, and ranking of safe operations.
- Limitation: Adopting key technologies (e.g., SAFs) remains quite pricey and has not been widespread.
- Mitigation Strategy: Rigorous risk assessment and adaptive management to address uncertainties (CRS Reports, n.d.)
b. Interdependency Among Industry Actors:
- Challenge: Airlines, OEMs, and suppliers depend on each other to achieve decarbonization commitments.
- Limitation: Over 95% of aircraft OEMs’ emissions come from airlines’ fuel burn (Scope 3 Category 11 downstream emissions).
- Mitigation Strategy: Collaborative efforts and industry-wide alignment to support airlines and offer solutions (Decarbonizing Aviation: Executing on Net-Zero Goals | McKinsey, n.d.)
c. Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies:
- Challenge: Implementing carbon reduction measures involves risks related to cost, technology adoption, and regulatory changes.
- Mitigation Strategies: Rigorous risk assessment, scenario planning, and adaptive management to address uncertainties.
- Example: UNDP’s Risk-Informed Development Strategy Tool guides the integration of disaster risk decrease and climate change adaptation into growth (Home | United Nations Development Programme, n.d.).
VI. CONCLUSION
In conclusion, Qatar Airways faces a defining crossroads where its response to carbon emissions and climate change will fundamentally impact its competitive positioning within the aviation industry for years. The issues it confronts, including high emissions intensity, limited access to sustainable aviation fuel, and negotiating efficiency with safety and performance, present formidable obstacles, though not insurmountable. The airline has already demonstrated foresight by launching a voluntary carbon offset initiative, promising to progressively blend sustainable aviation fuel into standard operations, refining fuel usage habits, and establishing environmental policies. Nevertheless, the escalating urgency of the climate crisis now demands bolder action without delay.
Failure to accelerate carbon reduction campaigns jeopardizes Qatar Airways’ reputation, legal compliance, and marketplace competitiveness. In contrast, embracing sustainable practices serves not just to enhance the airline’s public image but also boosts cost-effectiveness and long-term viability. To safeguard its position as a global aviation leader, Qatar Airways needs to accelerate work tapering carbon emissions. This necessitates further expenditure on sustainable technologies, expanding sustainable aviation fuel utilization, optimizing operational efficiency via innovative methods, and engaging passengers in carbon offset programs.
By guiding the industry on the way to a greener future, Qatar Airways can not only cement its competitive advantage but also contribute to the well-being of forthcoming generations and the health of our planet. The moment to act is upon us, and Qatar Airways possesses an opportunity to pioneer by example in structuring a more sustainable aviation industry.
REFERENCES
About Qatar Airways | Qatar Airways Newsroom. (2024, March 15). https://www.qatarairways.com/press-releases/en-WW/about/
Andrew Mills. (2023). Qatar Airways CEO suggests 2050 net-zero goal beyond reach | Reuters. https://www.reuters.com/business/aerospace-defense/qatar-airways-ceo-doubts-2050-net-zero-goal-can-be-reached-2023-05-23/
ATAG. (2021). Qatar Airways Group highlights environmental sustainability initiatives for World Environment Day: Aviation: Benefits Beyond Borders. https://aviationbenefits.org/newswire/2021/06/qatar-airways-group-highlights-environmental-sustainability-initiatives-for-world-environment-day/
Atul Jain. (2023). (25) The Future of Sustainable Aviation: Innovations and Initiatives | LinkedIn. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/future-sustainable-aviation-innovations-initiatives-atul-jain-/
Aviation Climate Action Plan | Federal Aviation Administration. (n.d.). Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.faa.gov/sustainability/aviation-climate-action-plan
Baluyut, J. (2022). Qatar pioneers study to find alternative fuel: Al Baker | The Peninsula Qatar. https://thepeninsulaqatar.com/article/22/06/2022/qatar-pioneers-study-to-find-alternative-fuel-al-baker
CRS Reports. (n.d.). Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://crsreports.congress.gov/
Decarbonizing aviation: Executing on net-zero goals | McKinsey. (n.d.). Retrieved April 2, 2024, fromhttps://www.mckinsey.com/industries/aerospace-and-defense/our-insights/decarbonizing-aviation-executing-on-net-zero-goals
Environmental sustainability | Qatar Airways. (n.d.). Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.qatarairways.com/en/about-qatar-airways/environmental-awareness.html
Hannah Ritchie. (2022). Climate change and flying: What share of global CO2 emissions come from aviation? – Our World in Data. https://ourworldindata.org/co2-emissions-from-aviation
Hayward, J. (2021, April 9). The Rise Of Qatar Airways: From Two A310s To Global Mega Airline. Simple Flying. https://simpleflying.com/rise-of-qatar-airways/
Home | United Nations Development Programme. (n.d.). Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.undp.org/
Joelyn Baluyut. (2023, August 19). Qatar Airways commits to sustainability, aligning with UN Goals. https://thepeninsulaqatar.com/article/19/08/2023/qatar-airways-commits-to-sustainability-aligning-with-un-goals
John, P. (2020, October 8). Qatar Airways’ fuel optimisation initiatives ensure improved efficiency, carbon reduction. Gulf Times. https://www.gulf-times.com/story/674881/qatar-airways-fuel-optimisation-initiatives-ensure-improved-efficiency-carbon-reduction
John, P. (2021, February 3). Qatar Airways’ key role in national economy; contributes 4.9% to country GDP. Gulf Times. https://www.gulf-times.com/story/683880/qatar-airways-key-role-in-national-economy-contributes-49-to-country-gdp
Laurie Bouchard. (2023, June 19). Canada invests $350 million in national sustainable aviation innovation network [News releases]. https://www.canada.ca/en/innovation-science-economic-development/news/2023/06/canada-invests-350-million-in-national-sustainable-aviation-innovation-network.html
Lomas, C. (2023, October 19). What is Sustainable Aviation Fuel? Flightradar24 Blog. https://www.flightradar24.com/blog/what-is-saf/
McCausland, R. (2023). Net zero 2050: Operational and infrastructure improvements.
Newspaper, T. P. (2020, November 3). Qatar Airways launches voluntary carbon offset programme for passengers. https://thepeninsulaqatar.com/article/03/11/2020/Qatar-Airways-launches-voluntary-carbon-offset-programme-for-passengers
Qatar Airways. (2022). Qatar Airways Group Releases 2021 Sustainability Report. Qatar Airways Newsroom. https://www.qatarairways.com/press-releases/en-WW/215116-qatar-airways-group-releases-2021-sustainability-report
Qatar Airways newsroom. (2022, April 21). Qatar Airways Launches Voluntary Carbon Offset Programme for its Corporate and Trade Clients. Qatar Airways Newsroom. https://www.qatarairways.com/press-releases/en-WW/215132-qatar-airways-launches-voluntary-carbon-offset-programme-for-its-corporate-and-trade-clients
Redactive Media Group. (n.d.). Welcome to Airlines—IATA’s Aviation Business Magazine. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://airlines.iata.org/
Reducing aviation’s impact on the climate—Environmental Defense Fund. (n.d.). Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.edf.org/climate/aviation
Rune, H. (n.d.). Aviation Carbon Offsetting.
Satyendra Pathak. (2022, September 22). QA committed to net-zero carbon emission by 2050, says Baker. Qatar Tribune. https://www.qatar-tribune.com/article/20973/business/qa-committed-to-net-zero-carbon-emission-by-2050-says-baker
Sustainable Aviation Fuel | Shell Global. (n.d.). Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.shell.com/business-customers/aviation/the-future-of-energy/sustainable-aviation-fuel.html
The digital evolution in aviation: How big data and analytics are transforming the industry. (n.d.). Cirium. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.datasciencecentral.com/the-digital-evolution-in-aviation-how-big-data-and-analytics-are-transforming-the-industry/
Vasigh, B., & Azadian, F. (2022). Aircraft Financial and Operational Efficiencies. In B. Vasigh & F. Azadian (Eds.), Aircraft Valuation in Volatile Market Conditions: Guiding Toward Profitability and Prosperity (pp. 113–163). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-82450-1_3
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:






