Introduction
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is one of the most common problems diagnosed in veterans of the United States. PTSD can be described as mental health problems that tend to develop and enhance after going through a life-threatening event or incident such as war combats, accidents, attacks, etc. If PTSD remains untreated for longer periods, it can create further psychological and physical complications such as cardiac issues, mental disorders, behavioral problems, etc. Veterans are the most common victims of PTSD. The impact of PTSD is usually intense on war veterans as they have undergone a series of traumatic incidents for longer periods of time that further involve feelings of guilt, aggression, repentance, revenge, vengeance, etc. Under such circumstances, it becomes extremely important that the veterans are provided with affordable and accessible Clinical facilities to improve their quality of life and psychological state.
Problem Statement
The Veterans of the United States must be provided with accessible and high-quality clinical facilities that specialize in the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of PTSD in veterans.
Scope
The scope of the proposal will cover the Veterans living in Naples, Florida. The reason for the definition of this scope is that Naples, Florida, houses the third highest population of Veterans in the United States with comparatively limited PTSD facilities.
Proposal Statement
Naples, Florida, must have state-of-the-art PTSD clinical centers specifically designated for the treatment and diagnosis of Veterans to improve their overall quality of life.
PTSD In Veterans
A few investigations of combat veterans with ceaseless posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) found that PTSD is related to high rates of self-announced physical symptoms in various organ frameworks (Schumm et al. 2013) and with an expanded utilization of medicinal administrations (Schumm et al. 2013). In the course of recent years have inspected the predictors of the diagnosis of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in Vietnam, Afghan and Iraq veterans; the attention has been on parts of fighters’ war encounters.
Combat involvement and exposure to harsh viciousness or abominations predict endless symptoms of PTSD (Schumm et al., 2013). A couple thinks about have inspected calculates other than war stressors that additionally put veterans at higher hazard for PTSD. Combat exposure and modification amid military administration predicted PTSD symptoms in a small gathering of treatment-chasing veterans, though a file of premilitary change did not (Lawson, 2016). The significant elements of that review in a national nonclinical test discovered similar outcomes, in spite of the fact that in both cases, the premilitary alteration variable was added last to the relapse condition. Different agents, as well, have observed war stressors to be the essential determinants of symptoms of PTSD, albeit different parts of prewar working may likewise add to current mental status (Lawson, 2016). Postwar elements that have been inspected and appeared to predict postwar change are negative life occasions and social backings (Lawson, 2016).
None of these specialists has included diagnoses other than PTSD while analyzing these hazard variables to investigate diagnostic cover and the discriminant legitimacy of the PTSD diagnosis. Military components assumed a bigger part than preservice elements (Lawson, 2016). For PTSD, military elements increasingly represented the change far beyond the commitment of pre-military elements. The essential givers to that set were exposure to abnormal demise. PTSD was the main diagnosis that was predicted by the life danger measure; the others were predicted principally by exposure to unusual demise. Freeze and phobic disorders were predicted by uncommon task exercises.
Therefore, while military components were a critical predictor of most diagnoses, the greatness of the commitment was moderately expansive just for PTSD and frenzy disorder (Lawson, 2016). Post-military variables contributed altogether to a diagnosis of PTSD, well beyond the commitments of pre-military and military components (Schumm et al. 2013). They likewise clarified the critical difference in the diagnoses of significant depression and liquor and medication mishandling (Schumm et al. 2013).
For PTSD, both support at homecoming and current bolster diminished the probability of a PTSD diagnosis. Current support was additionally connected with a lesser probability of significant depression and medication manhandling. None of the factors predicted liquor manhandling alone, yet together, they added essentially to the likelihood of that diagnosis. The three sorts of hazard elements combined clarified the most difference for PTSD, trailed by liquor mishandling, real depression, and frenzy disorder.
Therefore, manhandling and summed-up tension disorder were the slightest predicted by the factors under examination. The war stressor variables were exceptionally predictive of PTSD and contributed firmly to frenzy disorder. The most grounded predictor of PTSD, and of a large portion of alternate diagnoses, was exposure to bizarre passing. This variable, which incorporates exercises subsumed under oppressive savagery or outrages, has been involved by different specialists as an essential determinant of proceeding with symptoms of PTSD.
Furthermore, the Postwar components, particularly social support, assumed an especially vital part in the prediction of PTSD. Bolster at homecoming fundamentally diminished the danger of creating and keeping on having PTSD. In any case, bolster likewise relied upon a trooper’s war understanding, which appeared to impact his openness to associating with others and may, in fact, mirror the distance/separation that is a piece of the PTSD diagnostic criteria.
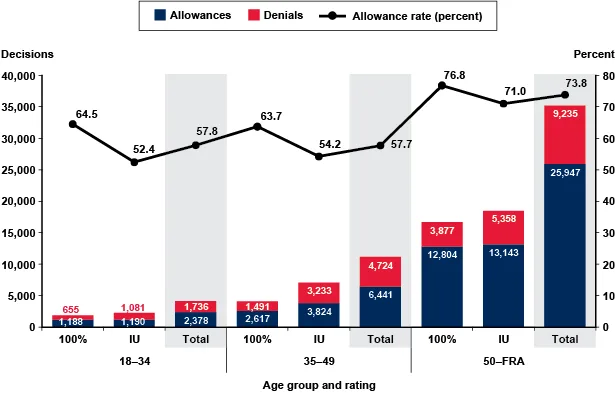
Following are the statistics for PTSD allowances currently. And these numbers are not very encouraging.
Moreover, the individual with persevering PTSD additionally had less present support than the individual without PTSD, which thus was predicted by war encounters, recommending that the very stressed survivor keeps on feeling disconnected and will most likely be unable to access bolster regardless of the possibility that it is accessible. On the other hand, a man with ceaseless and disruptive symptoms that have most likely been present since the war may have figured out how to distance family and companions after some time. Regardless, PTSD and a few different diagnoses were altogether predicted by current support, showing that notwithstanding the war understanding, a strong system diminishes the danger of postwar issues.
Social backing, funding and support improved recuperation, yet the ability to make utilization of accessible social bolster appeared to depend on, in any event to a limited extent, on the nature and force of a trooper’s war involvement. Taken together, the discoveries demonstrate that PTSD was essentially connected to stressful encounters for this gathering of survivors and that it was more connected with these encounters than were alternate diagnoses and symptoms analyzed.
Need For Significant PTSD Centers
Furthermore, the symptoms associated with PTSD in veterans are regularly connected with an extensive variety of intense psychological distress and psychiatric comorbidity, low quality of life, and extreme social maladjustment. The disorder is profoundly prevalent in American VA Medical Centers.
There are more than 5-million surviving American veterans of outside wars, the potential number of veterans right now with PTSD is well over the half-million check. The medicinal framework comes to the weight of giving mental well-being, restorative, social, and disability administrations to countless with extreme PTSD and other related mental sicknesses.
The expenses related to PTSD, both to people and society, are, to a great degree, high. Compared to most other psychiatric disorders, PTSD in the overall public is related to higher rates of administration utilization and higher medicinal and social expenses. In studies, PTSD has been related to more noteworthy therapeutic sickness comorbidity.
On average, almost two million troops have been deployed to the contentions in Iraq and Afghanistan since September 2001 (Reisman, 2016). Almost 30% of troops came back with mental medical issues, prompting post-deployment adjustment troubles (Reisman, 2016). Reports have documented expanding rates of PTSD, uneasiness disorders, depression, and substance utilization disorders among veterans.
In spite of the fact that the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) and U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) offer alternatives for treatment, numerous veterans and military staff who have PTSD or other mental disorders don’t get mental well-being treatment. Just a single quarter of dynamic obligation troops with psychiatric diagnoses get treatment administrations. Furthermore, among the individuals who do look for treatment, many don’t get proven treatments or a satisfactory measure of them. This circumstance represents an open door for improvement.
Discoveries from previous reviews have demonstrated that shame adds to the negative perspective of mental well-being treatment among troops. Shame, including self-disgrace, open shame, and disgrace inside an administration part’s unit, is the main consideration in low treatment usage. The impression of administration accessibility and individual convictions about treatment likewise have been accounted for as barriers to mind. Veterans, too, have announced obstructions in connecting with the VA, for example, bothers with booking, waiting for circumstances, transportation, and exploring the medicinal services framework all il.
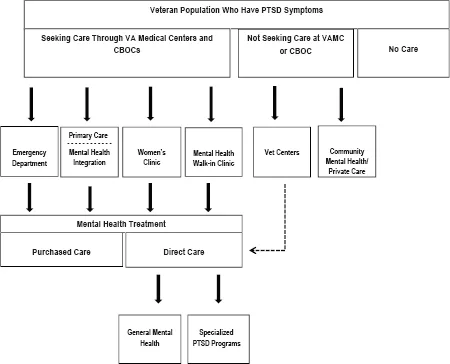
Figure: Behavioral Response of PTSD Suffering Patients for Seeking Treatment[1]
Veterans In Naples, Florida
For establishing state-of-the-art PTSD Clinical centers, Naples, Florida, appears to be the ideal situation. The reason for stating so is that it is the third highest populated region with Veterans. According to the Organization of Veterans of Florida, the following image presents an overview regarding the statistical representation of the diversity of the Veteran population.
Figure: Statistics of Veterans in Florida
Comparing the above-presented statistics with the current condition and situation of the veterans in Florida, the situation is not very acceptable. Regardless of having a massive Veteran population, there are no proper social support services for the Veterans. According to the figures presented by the Department of Veterans Affairs and the Florida Department of Veterans Affairs, a devastating overview can be established.
According to the statistics, there are almost 8,493,700 veterans in Florida who have received services from the VA since 2008. This makes them almost 36% of the total living veteran population of the United States. However, what is more disturbing is that out Of these veterans, almost 70% of them are receiving services from one program, which is not sufficient to meet the needs and requirements of Veterans who may already be suffering from issues like PTSD. The results become more alarming to know that almost 33% of all Veterans need assistance for health care services that include PTSD, too. Under such circumstances where the social services, funds, and health care facilities for the veterans are scarce, it is important to establish clinical facilities that are accessible and affordable for the veterans suffering from PTSD.
Involved Risks For Improper Diagnosis And Clinical Facilities
PTSD is also related to physical agony symptoms, also. For veterans coming back from Iraq and Afghanistan, constant agony keeps on being a standout amongst the most often announced symptoms. Around 30% of patients with unending torment additionally have PTSD (Reisman, 2016).
Barriers And Challenges For High-Quality Treatment Facilities
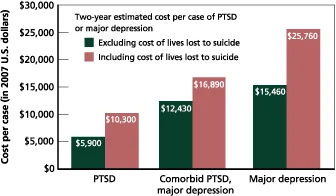
The requirement for better arrangements appears by the immense monetary and societal weight of PTSD, i.e., about $8,300 per individual per veteran (Reisman, 2016). The following images will help to understand the overall expense and burden of PTSD treatments for Veterans.
Furthermore, the following shows individual costs for only two years of time.
Regardless of endeavors to build access to proper mental and social insurance, numerous military veterans keep on facing barriers to getting PTSD treatment. The biggest single barrier to auspicious access to mind, as per a VA review, is the absence of supplier appointment accessibility (Taylor et al. 2013). An intense lack of specialists in the VA, especially in essential care, combined with the rising populace of veterans looking for treatment, has prompted months-long holding up times (Taylor et al. 2013).
As indicated, the veterans from these zones are more likely than urban veterans to get to mental well-being administrations, to a limited extent, because of the more noteworthy distances they should travel (Taylor et al. 2013).
A standout amongst the most much of the time referred to barriers to veterans getting opportune and sufficient tend to PTSD is the social shame related to mental disease (Roberts, 2016). Examine shows that administration individuals may feel embarrassed and embarrassed to look for treatment, see mental ailment as an indication of a shortcoming, or feel that it is possible to dispose of it (Roberts, 2016).
Recommendation: Accessible And State Of Art Clinical Facility
Considering the risks, threats, and barriers faced by Veterans to seek quality treatment for PTSD, it is important that specialized clinics must be established within the accessible vicinity that are capable of providing immediate care to war veterans. The proposed accessible clinic for the PTSD-suffering veterans will include the following features:
- Authorized with the standards of PTSD identified and regulated by the Department of VA and concerned Health Care authorities.
- Easy to Access health care centers that may also have the facility of Tele-pathy or eServices for the patients who may not be able to travel or have personal issues to visit the clinical facility.
- The centers will be able to treat inpatients as well as Outpatients.
- The health care providers will specialize in PTSD associated with veterans only.
- The centers will be authorized by government funding departments as well as local funding and charity organizations to ensure that the economic burden is lifted off the PTSD-suffering Veteran patients and their families.
- The organization of the Clinical Facilities will be in accordance with the standard specified by VA, as shown in the figure below:
Most prominently, the veterans displayed an egoistic and emotional attitude where they feared of being called coward or pshyco patients if they express their PTSD status or similar disorders.. One system to lower this worry of veterans with PTSD is to make accessible successful, proven behavioral treatment for PTSD, for example, delayed exposure or intellectual handling treatment, for veterans who don’t wish to take medications.
Similarly vital is training and media awareness that addresses veterans and accentuates that treatment may take diverse structures, including approaches that do and don’t require medications. In a joint effort with such endeavors, it will be imperative that veterans with PTSD symptoms who look for care are given decisions or are alluded to suppliers who will settle on accessible decisions.
Moreover, the stability of “Emotions” was likewise a common barrier to looking for treatment, as detailed by a few of the members. This class encompassed two sorts of concerns: the discernment that discussing troubles would incite an abnormal state of nervousness, subsequently making a motivation to dodge or defer treatment, and the worry that they didn’t require treatment and preferred some possibly maladaptive adapting systems. Media battles may help on the off chance that they stress that treatment gives a protected environment where people can work at their particular pace, that confirmation-based treatments for PTSD help decrease symptoms, and that staying away from traumatic memories and the related uneasiness adds to, or even increments, progressing challenges.
The last barrier might be hard to overcome. For instance, a few veterans see their liquor use as helping them adapt. This adapting aptitude might be viable on a transitory premise, yet if utilized long-term, it might prompt different issues. Veterans ought to be urged to fabricate their collection of adapting abilities so they can adequately oversee symptoms without over-relying on one, particularly if that adapting expertise is possibly unsafe.
A potential clarification for the low prevalence of worries about shame is that battles focusing on disgrace have had some positive effects. Earlier reviews on treatment looked for having, to a great extent, concentrated on disgrace, possibly setting the phase for decisions about the significance of decreasing shame. It is likewise possible that the relative absence of concern for shame identifies with a more extensive pattern of developing acknowledgment of mental well-being diagnoses and treatments in the U.S. populace. This impact may have been opened up by the adolescent because more youthful veterans might not have been exposed to the previous era’s dispositions toward treatment.
In this way, keeping in mind the end goal to increment mental well-being treatment looking for among veterans coming back from obligation with PTSD symptoms, suppliers should first clear up for veterans what they can anticipate from treatment and the treatment alternatives accessible and address their worries about the availability for treatment. Our outcomes recommend that tending to shame and strategic barriers are, to some degree, less critical in this exertion.
Discussion
Therefore, it can be said that while numerous vital advancements have been made in the course of recent decades in comprehension and treating symptoms of PTSD, the rising number of American veterans who experience the ill effects of the disorder keeps on being a genuine national general medical issue. Intellectual, behavioral treatment is an acknowledged technique for the treatment of PTSD, yet there is obviously a dire need to recognize more viable pharmacological methodologies for the management of symptoms, as not all patients will react enough to psychotherapy or pharmacotherapy. Additionally, comprehension of the fundamental physiological and neurological procedures will be useful in growing new and successful treatments to treat PTSD.
References
Reisman, M. (2016). PTSD Treatment for Veterans: What’s Working, What’s New, and What’s Next. Pharmacy and Therapeutics, 41(10), 623.
Schumm, J. A., Fredman, S. J., Monson, C. M., & Chard, K. M. (2013). Cognitive-behavioral conjoint therapy for PTSD: Initial findings for Operations Enduring and Iraqi Freedom male combat veterans and their partners. The American Journal of Family Therapy, 41(4), 277-287.
Lawson, T. (2016). Accommodating Military Student-veterans, PTSD, and Post-Secondary Education (Doctoral dissertation, COLORADO TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY).
Taylor, M. F., Edwards, M. E., & Pooley, J. A. (2013). “Nudging them back to reality”: toward a growing public acceptance of the role dogs fulfill in ameliorating contemporary veterans’ PTSD symptoms. Anthrozoös, 26(4), 593-611.
Roberts, P. E. (2016). MISSION CRITICAL VETERANS HEALTH SUMMIT: ADDRESSING THE INVISIBLE WOUNDS OF OUR NATION’S VETERANS: PTSD, TBI, AND OTH DISCHARGES: A CASE STUDY OF A YOUNG SERVICE MEMBER. Hofstra L. Rev., 45, 35-331.
Roberge, E. M., Allen, N. J., Taylor, J. W., & Bryan, C. J. (2016). Relationship Functioning in Vietnam Veteran Couples: The Roles of PTSD and Anger. Journal of clinical psychology, 72(9), 966-974
Cite This Work
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below: