Introduction
A strong governmental power can make a country strong, peaceful and bring the economic growth. Opposite, a weak governmental power can make a country weak, unpeaceful, poor and even cause the wars. Mexico is a country has abundant resources, high labor force, and an excellent location which is closed to North America. On the other hands, at the same time, Mexico’s society is very unstable, high crime rate, and poverty. People elect their government and wish the government can bring them a stable, peaceful, and economic growth in future. But, obviously Mexican government do not do that, the drug violence, human trafficking, and gun smuggling problems are still there [1]. According to the research, drug violence area is spreading, even the drug violence rate is declined along with the US – Mexico border, but in the south of Mexico, it is increasing[2] . The Mexican government also has corruption problem; it makes people untrusted their government and public institutions. Then the governors are getting harder and harder to do their tasks [3]. In this research paper, I want to discuss what happened to Mexico government and its governmental power. The government should give their people a stable life without war, but Mexico government fail to do that. What is wrong with Mexico governmental structure?. The paper aims to examine the factors that affect the stability of the government structure.
Discussion
Legislative Structure
The legislative branch of Mexican government constitutes of two divisions, upper and lower. Top division is Senate, and lower division is Chamber of deputies. By comparing these divisions with the divisions of USA, both have same purposes, approval of legislation and ratification of upper-level presidential appointments. In practice, the executives initiate around 90% of all law. Every year Congress holds to sessions. The first session starts and ends in the period of November 1 till December 31. However, the second session begins and ends in between the period of April 15 to July 15. 37 members of a permanent committee assume the legislative responsibilities during congressional recesses. In the past, Senate consisted of 64 members. From these sixty-four members, two members appointed that will represent federal district and two will be selected to each state of the country. The term for these appointments used to be six years. In 1193, size of Senate became double with the members of total 128. After 1986, lower division of the government consisted of 500 members, from these 500, 200 were selected by the representatives of different districts.
The primary power of Congress includes the right to impose taxes, pass laws, approval of the national budget, declare war, conventions made with foreign countries and approval or rejection of treaties. The lower division of the government is as similar as the US house of representatives that identifies all issues that are more closely related to the government’s budget. Deputies of the chamber have the power to elect the provincial president. Every legislative council has its committee that examine and propose bills. However, if there is any conflict arise between the chambers, then a compromised version of a draft will be given by the joint committee.
Judicial Structure
In Mexican government, Judicial system is divided into state and federal systems. The highest court of Mexico is the Supreme court of justice. It consists of 21 magistrates along with five auxiliary judges. The president appoints these members and approved by the parliament or Senate committee. Eligibility criteria s straightforward person should be a Mexican citizen, must be an age of between 35 to 65 years and should have a law degree. Mexican constitution explains that the appointment of judges is for the life time, however, can be replaced by the Chamber of deputies. The meetings of these judges vary with the nature of cases. One argument that is raised on the judicial system is based on the fact that judicial system for big giants is different from the judicial system for average or poor people of Mexico. Which raise the question of the fairness of the judicial system. One of the articles published shows the unfairness and avoidance of public appeals in the judicial system in Mexico. Although amendments are done in the judicial system to make it fair in all aspects but to reach its fairness it will take more than 11 years to incorporate pure and fair justice in the society [4].
The judicial system presented by the government depicts its fairness but reality way too different. Another study reveals that the crime rate is increasing with high speed in Mexico, but the government has failed to stop that crime even the judicial system that should punish the criminals has its eyes closed on these matters and its reforms are in great danger. However new reforms have been provided. For instance, in 2008, Congress of Mexico approved a series of reforms that established adversarial court proceedings and effective legal protection for criminal defendants, how ver, these reforms are not successfully implemented if it does then crime rate should have reduced down rather then going up [5].
According to the article 155 of the criminal code in the judicial system that explains the use of bracelets and ankle to measure eth precautionary measure of a risk person. Although this is mentioned in the constitution, still there are no prisons that have such tools. There is no evidence that the prisons are using these. Precautionary measure are still not prevailing in Mexico which should have been. According to the director of Criminal Procedural justice institute, there is a need to strengthen precautionary measures [6].
There are many cases reported and published n media of Mexico that represents the poor and unfair treatment of the courts to the innocent people. For any government, the judicial system plays the role of a backbone. In past times, Mexican trials were conducted on the basis of writing, witnesses, with victims and it, has been seen that lawyers didn’t have access to the judge, now this is the system that will presume guilt over innocence which ultimately gives prosecutor a vast power [7].
State Government
Mexico has 31 states and a federal district that encompasses Mexico. Every country in Mexico has its constitutions that are modeled on the national charter. At the national level, both the state and local government have their executives and judicial branches. The primary function of the state government is to legislate and levy taxes on customs duties. Other then the fact that political system of Mexico is highly centralized which means that all the decision made at the central hub of the government. The state government is mostly dependant on the revenues from the Mexico city. Governor is the one that handles the executive branch of the state. The majority votes directly elect a governor for a term of six years. Just like the president, the governor cannot be reelected. Most of the legislative bills are represented by the deputies, state superior court of justice and by the state governor. However, in some cases by the municipality within the particular state. Supreme court of justice heads the state judiciary. The federal district has its local courts and representative assembly, which is elected by the proportional representation. In the past, assembly was considered a local body that doesn’t have any legislative power.
Local Government
Local government is considered one of the basic units of the Mexican government. There are more than 2000 municipal governments in Mexico. These governments are mainly responsible for multiple public services that include street lighting, water, and sewage, public safety, and traffic, maintenance of parks, cemeteries and cleaning and maintenance. Every municipal government is run by the mayor that is selected for the term of 3 years. Local governments are authorized to collect taxes, but they are failed to do so in the past. Municipality government are free to assist state and federal governments associated with the issue is education, medical services and emergency fire [8].
Following are some graphs taken from the World Bank statistics that show the effectiveness of the political system in Mexico along with corruption, the rule of law and government effectiveness.
Source: World Bank
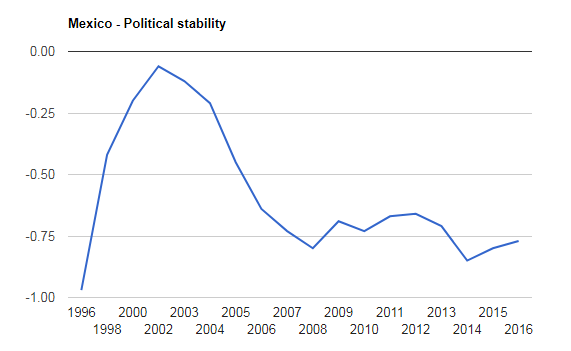
Above chart shows the political stability of Mexico. Parameter ranges from -2.5 to 2.5 in which -2.5 shows weak political stability while 2.5 shows strong political stability. The data are taken from 1996 to 2016. One can see that from the period of 1996 to 2016, there was no single year in which country’s political position went to stability. It is always in a negative figure.
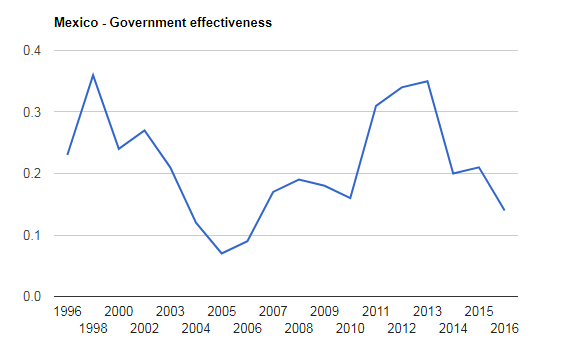
The graph presented above show the effectiveness of Mexican government from the period of 1996 to 2016. This chart shows that government has been found useful in 1998 with 0.35 points, but after 1998 it dropped down in coming years until it rises again in 2013 and 2014. However, in 2016, world bank gave the effectiveness points of 0.15 which shows the moderate effectiveness of government. The efficiency of government is associated with the quality of civil services, quality of public service and degree of its independence from political pressures.
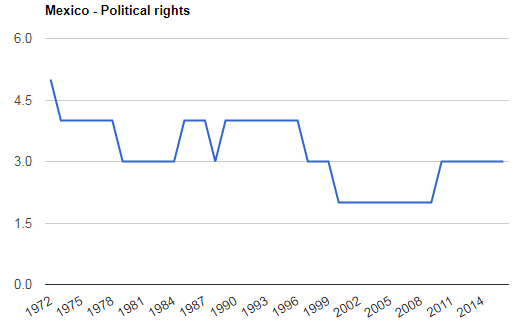
The graph shown above shows the effectiveness of political rights in Mexico. The range standard was from 1 to 7 points in which 1 indicates the weak political rights while 7 shows strong political rights. This index measured on the data from 1972 to 2014, the average value for Mexico is 3 points while it was high in 1972 with 5 points. Three categories have been evaluated in measuring the politics rights index, political pluralism, participation and electoral process. From the graph, one can say that in the start Mexico had strong political rights provided and with the passage of time it dropped down to 3 points in 2014 which shows the inefficiency of rights.
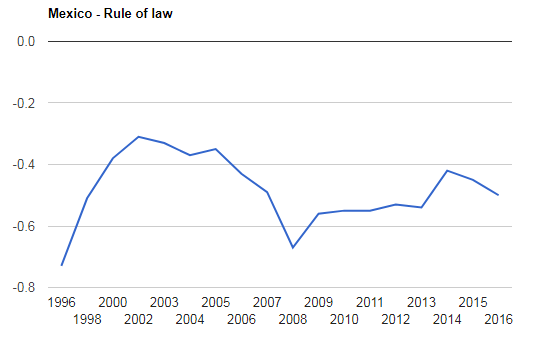
Above graph shows the index rule of law from 1996 to 2016. In the figure -2.5 shows the weak rule of law while 2.5 shows the strong rule of law. The index captures the perception to the extent to which agents have confidence and trust in and abide by the rules of society, property rights, the courts, the police and likelihood of crimes. The average value for Mexico in the defined period was -0.48 points which show the weak rule of law in Mexico.
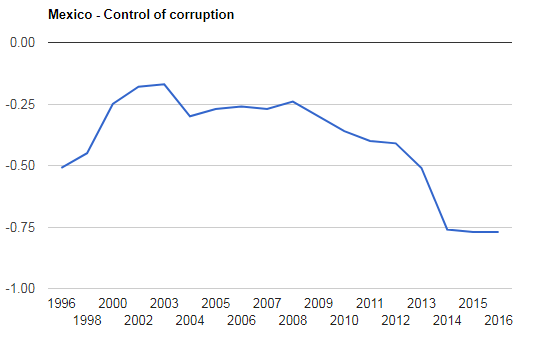
The graph shown above represents control of corruption by the government of Mexico from the period of 1996 to 2016. -2.5 shows the weak efforts while 2.5 shows strong efforts by the government in the reduction of corruption from the country. The average value for the corruption control is -0.48 points which mean the government was inefficient to reduce corruption in the country. The index captures the perception of the extent to which the top officials of the government exercise public power for their private gains and motives [9].
- Morris, Stephen D. Corruption & politics in contemporary Mexico. University of Alabama Press, 1991. ↑
- . Molzahn, Cory, Viridiana Ríos, and David A. Shirk. “Drug violence in Mexico: Data and analysis through 2011.” Trans-Border Institute, University of San Diego, San Diego (2012). ↑
- Morris, Stephen D., and Joseph L. Klesner. “Corruption and trust: Theoretical considerations and evidence from Mexico.” Comparative Political Studies 43.10 (2010): 1258-1285. ↑
- Mexico has spent eight years overhauling its dysfunctional justice system, but it may need 11 more to fix the mess. 2018. “Mexico Has Spent 8 Years Overhauling Its Dysfunctional Justice System, But It May Need 11 More To Fix The Mess”. Business Insider. Accessed April 23, 2018. http://www.businessinsider.com/mexico-needs-11-more-years-to-reform-justice-system-2016-5. ↑
- SHIRK, OCTAVIO. 2018. “Mexico’S Badly Needed Justice Reforms Are In Peril.” Sandiegouniontribune.Com. Accessed April 23, 2018. http://www.sandiegouniontribune.com/opinion/commentary/sd-mexico-justice-utak-commentary-20170811-story.html. ↑
- “Six Shortcomings Of Mexico’s New Justice System.” 2017. Insight Crime. Accessed April 23, 2018. https://www.insightcrime.org/news/analysis/six-shortcomings-of-mexico-new-accusatory-criminal-system-according-to-experts/. ↑
- “In Mexico, A Justice System Where ‘Citizens Are Heard’ Starts To Take Root”. 2016. The Christian Science Monitor. Accessed April 23, 2018. https://www.csmonitor.com/World/Americas/2016/0601/In-Mexico-a-justice-system-where-citizens-are-heard-starts-to-take-root. ↑
- “Mexico – Government Structure.” 2018. Countrystudies.Us. Accessed April 23, 2018. http://countrystudies.us/mexico/82.htm. ↑
- “Mexico | Data.” 2018. Data.Worldbank.Org. Accessed April 23, 2018. https://data.worldbank.org/country/mexico?view=chart. ↑