Sickle Cell Anemia, Pearson syndrome, Duchene Muscular Dystrophy, lactose intolerance, Familial Breast Cancer, polycystic disease, and Huntington’s multiple repeats are some of the most serious genetic disorders. This paper gives an overview of the profile of each disease.
- Sickle Cell Anemia
- Name of Disease: Sickle Cell Anemia SNP based.
- Nomenclature
- Phenotype MIM number: 603903
- Gene locus MIM number: 141900
- Gene Symbol: HBB
- Normal function of gene: It encodes for the formation of beta globin subunits.
- Brief Description:
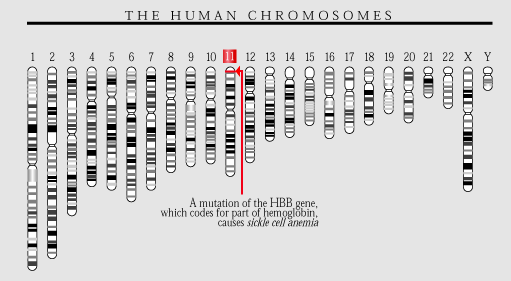
It is a disease of the red blood cells resulting from gene mutation on HBB gene. HBB gene is found in chromosome 11 and encodes for beta globin. The mutation results in formation of HbS and incapacitates the oxygen-carrying capacity of the red blood cells. The disorder causes varied degrees of anemia.
- Chromosome location and gene coordinates: HBB gene on Chromosome 11
Figure 1: Chromosome location for Sickle cell anemia
- Inheritance Pattern:
The disease is recessive trait. Phenotypic expression of the disease occurs when a person inherits two recessive genes from both parents so that they are homozygotes.
- Genetic basis:
Gene mutation causes formation of sickle-shaped cells with reduced capacity to transport oxygen.
- Interesting fact:
The disease was discovered in 1910 but that does not imply that the disease never existed before. It has been in existence for thousands of years. The nature of the disease became clear in the 1950s.
- Pearson Syndrome
- Name of Disease: Pearson Syndrome.
- Nomenclature
- Phenotype MIM number: 612623
- Gene locus MIM number: 133170
- Gene Symbol: EPO
- Normal function of gene: hematopoiesis and normal functioning of mitochondria.
- Brief Description:
The disorder affects multiple organs and systems in the body, especially the pancreas and bone marrow. This interferes with hematopoietic stem cells hence defective formation of blood cells. It also affects mitochondrial DNA, making respiration difficult.
- Chromosome location and gene coordinates: 7q22.1
Figure 2: Chromosome affected by Pearson syndrome
- Inheritance Pattern:
The mutations that cause Pearson syndrome occur spontaneously in the offspring.
- Genetic basis:
Multiple gene mutations cause defective erythropoiesis, faulty mitochondrial enzyme formation and defective pancreas function.
- Interesting fact:
Howard Pearson was the first person to describe the syndrome in 1979. Hence the condition was named after him. Pearson was a pediatric oncologist and hematologist.
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
- Name of Disease: Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.
- Nomenclature
- Phenotype MIM number: 310200
- Gene locus MIM number: 300377
- Gene Symbol: DMA
- Normal function of gene: encodes for formation of dystrophin protein that helps in muscle contraction and in nerve function. The protein works together with other proteins to strengthen muscle fibers.
- Brief Description:
The disorder causes progressive weakness and degeneration of muscles due to lack of dystrophin protein.
- Chromosome location and gene coordinates: Xp21.1
Figure 3: Chromosome location for Duchene Muscular dystrophy.
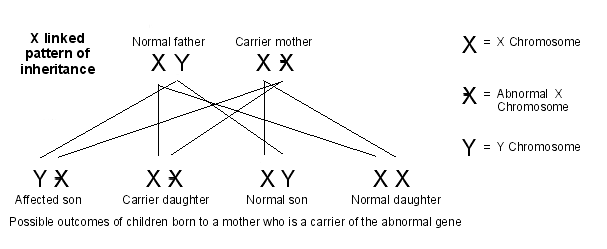
- Inheritance Pattern:
X-linked inheritance pattern
- Genetic basis:
The condition is linked to X chromosome and is inherited alongside it. Since males have only one X chromosome, the condition is more prevalent in males than females.
- Interesting fact:
The disease was first reported in 1836 by Gioja and Conte who identified it in brothers who had progressive muscle degeneration from age 10.
- Lactose Intolerance.
- Name of Disease: lactose Intolerance.
- Nomenclature
- Phenotype MIM number: 223100
- Gene locus MIM number: 601806
- Gene Symbol: LCT
- Normal function of gene: LCT gene encodes for the formation of lactase enzyme which is responsible for the digestion of lactose.
- Brief Description:
Mutation on LCT gene result in formation of abnormally short lactase enzyme, incapable of carrying out the normal functions of the enzyme.
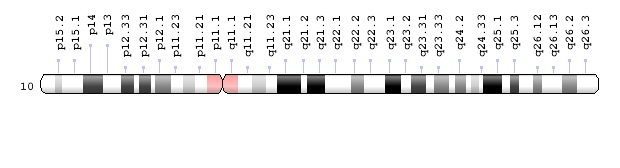
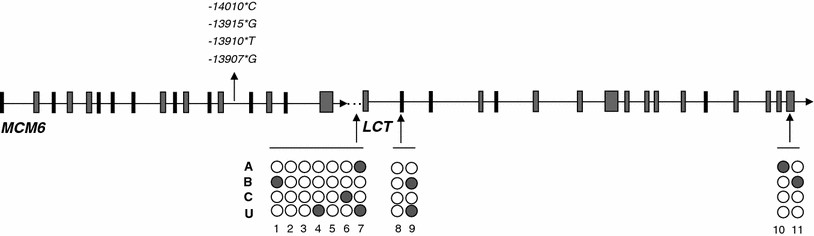
- Chromosome location and gene coordinates: 2q21.3 located in MCM6
Figure 4: Chromosome location for LCT gene
- Inheritance Pattern:
Autosomal Dominant pattern.
- Genetic basis:
It is a recessive trait which is expressed only by homozygotes with cytosine residues on the alleles adjacent to lactase gene.
Interesting fact:
More than 75% of the global population suffer lactose intolerance and cannot consume milk and milk products in adulthood.
- Lactose Intolerance.
- Name of Disease: Familial breast cancer.
- Nomenclature
- Phenotype MIM number: 114480
- Gene locus MIM number: 600185 for BCRA2 and 603615 for RAD54L
- Gene Symbol: BRCA2
- Normal function of gene: BRCA2 gene regulates DNA repair of damaged DNA by producing BRCA2 protein.
- Brief Description:
BCRA2 is responsible for up to 10% of breast cancers. Defects in this gene are inherited along familial line.
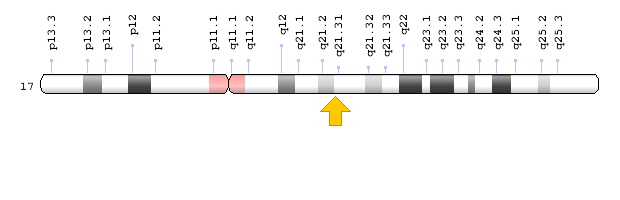
- Chromosome location and gene coordinates: 17q21.31
Figure 5: Chromosome location for BRCA2 gene
- Inheritance Pattern:
Autosomal Dominant pattern.
- Genetic basis:
Mutation on gene locus for BRCA1.
Interesting fact:
Family history of breast cancer has been noticed in more than 21% of people with breast cancer.
- Polycystic Kidney Disease.
- Name of Disease: Polycystic Kidney Disease.
- Nomenclature
- Phenotype MIM number: 173900
- Gene locus MIM number: 601313
- Gene Symbol: PKD1
- Normal function of gene: PKD1 encodes for polycystin-1 which is very active during prenatal life.
- Brief Description:
In polycystic kidney disease, numerous fluid-filled cysts grow in the kidney. These cysts may eventually damage the kidneys and orchestrate kidney failure.
- Chromosome location and gene coordinates:
16p13.3
- Inheritance Pattern:
Autosomal Dominant pattern.
- Genetic basis:
Mutation in PKD1 gene.
Interesting fact:
Most end-stage kidney diseases eventuate from PKD. The disease was first identified in 1586 by Jan Zigulist.
- Huntington’s Multiple Repeats.
- Name of Disease: Huntington’s multiple repeats.
- Nomenclature
- Phenotype MIM number: 143100
- Gene locus MIM number: 613004
- Gene Symbol: HTT
- Normal function of gene: The HTT gene encodes for the protein huntingtin. The protein ensures that brain neurons develop normally during prenatal life.
- Brief Description:
The disease makes brain neurons to degenerate progressively, with symptoms beginning to develop at around 40 years of age.
- Chromosome location and gene coordinates:
4p16.3
- Inheritance Pattern:
Autosomal Dominant pattern.
- Genetic basis:
HTT gene causes a repeat of the CAG trinucleotide. In normal people, the segment repeats only about 35 times while in people with Huntington disease, the HTT gene mutates causing the segment to repeat up to 120 times.
Interesting fact:
The disease mainly affects the basal ganglia of the brain. Dr. Huntington George was the first to describe the disease and more than 80% of people with the condition have chorea as well. Hence, the name Huntington’s chorea.